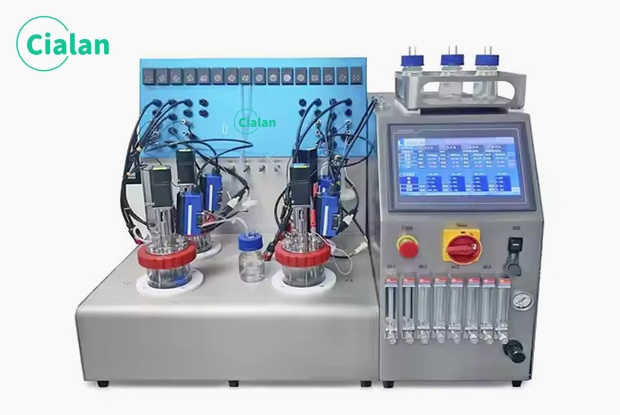
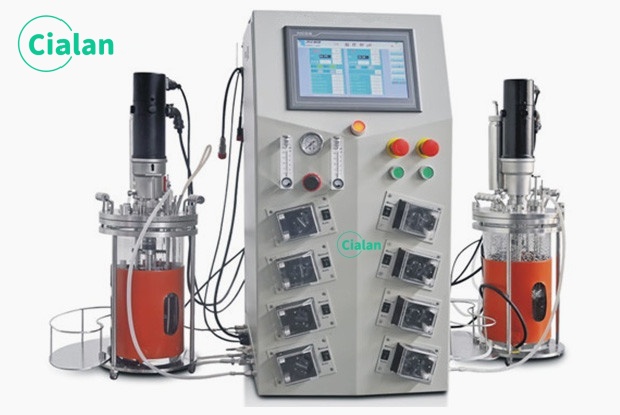
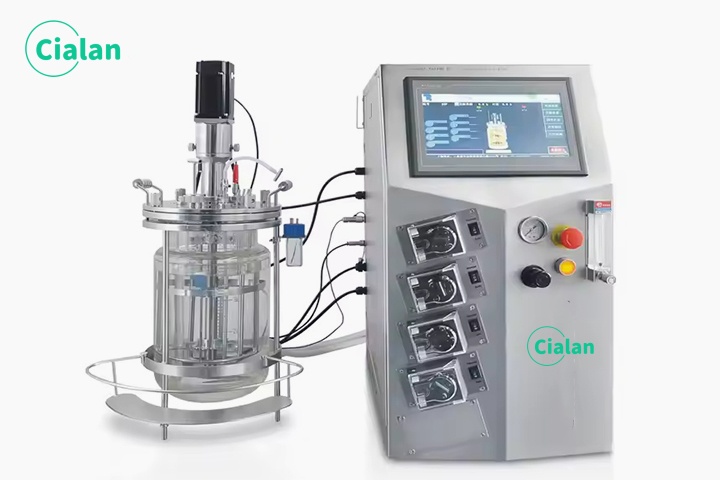
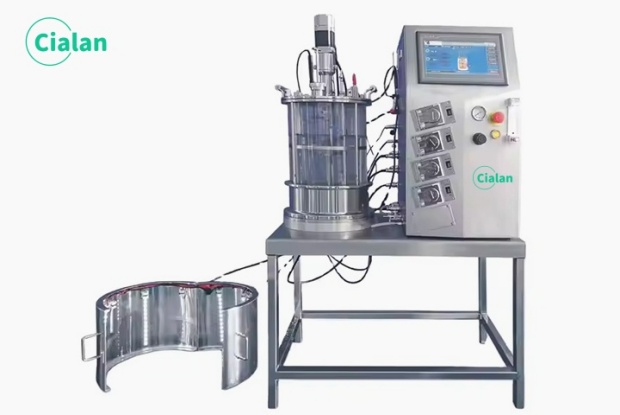
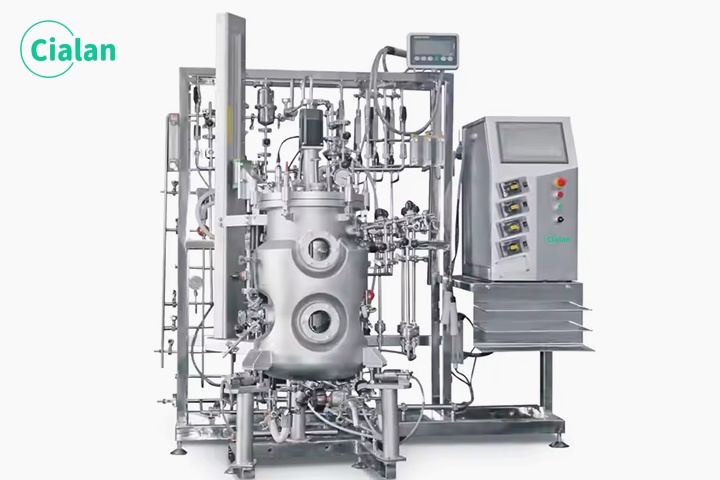
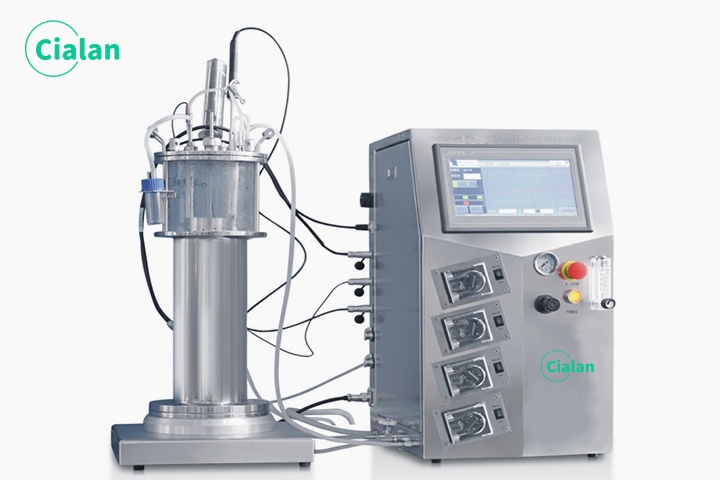
Fermenter bioreactor FAQ guide: Key insight for buyers in fermentation process.
Are you considering adding a bioreactors to your laboratory or factory? As a lab or factory investor, researcher, or equipment purchasing expert, our comprehensive articles will provide you with all the insight you need.
In this engaging blog, we'll explore the most common questions about bioreactors such as pricing, types, maintenance, applications and principles. You'll discover how these sophisticated fermentation tank can enhance the accuracy of your bioprocessing results and increase the yield of your fermentation products.
By reading the FAQ guide, you will discover valuable advice on choosing the perfect bioreactor to match your lab or factory. In addition, we share tips on how to choose a reputable manufacturer, understand the difference between bioreactors and fermenters, how to use these products, and how to utilize these bioreactors for a more stable biological culture process.
Whether you are in a lab where cells and microorganisms are cultured or a plant where fermentation products are produced, you will find everything you need here.
Bioreactors are a central tool in the field of bioengineering, covering areas such as food, agriculture, scientific research, industrial production, healthcare, environmental protection and social sustainability. Consulting with bioreactor manufacturers and application specialists can help you decide which system is best suited for your specific needs.
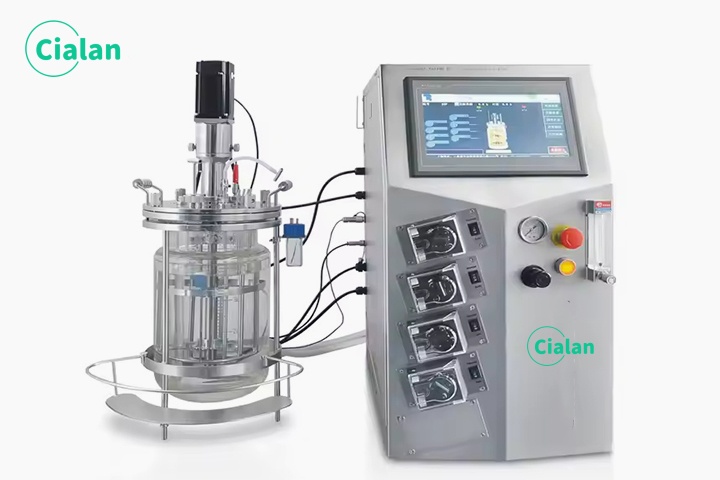

What Is A Bioreactor?
BIoreactors definition in biology as a device used to culture cells or microorganisms under controlled conditions. This includes the cultivation of various types of animal, plant and human cells, as well as the fermentation of bacteria, yeast and fungi. etc.
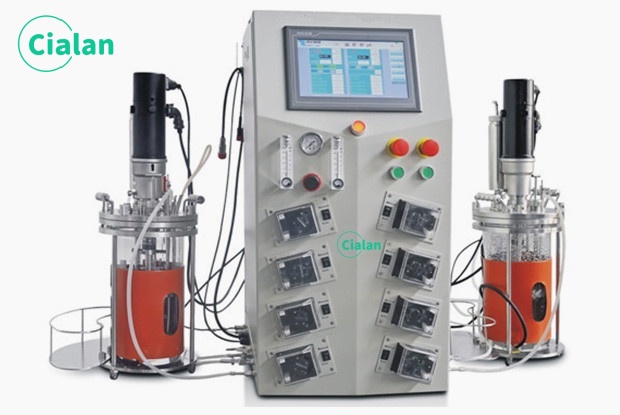

What Is A Fermenter?
Fermenters are closed vessels specially designed for the microbial fermentation process to produce a variety of fermentation products. Such as fermentation foods, beverages, beer, Lactic acid bacteria, yeast, alcohol, dairy products etc.
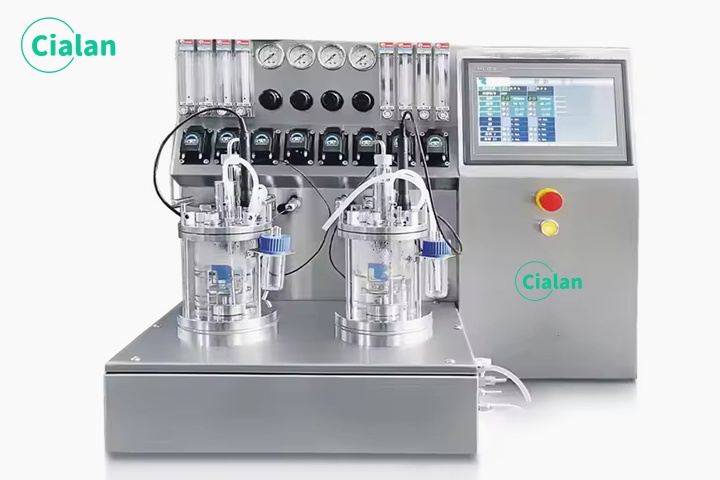

What Is The Difference Between Bioreactor And Fermenter?
Application: Bioreactor tank can be used for various biological processes, including tissue engineering, mammalian cell culture, etc. While fermenter tank is mainly used for microbial fermentation, such as bacteria, yeast or fungi, and producing fermentation products, which is a kind of bioreactor.
Design and Construction: Bioreactors have more advanced and complex control systems. Often designed with specific features to meet the needs of fermenting organisms.
Size: Bioreactors can be designed in different shapes and sizes depending on the application; fermenter vessel is usually conical or cylindrical and have a larger capacity than bioreactor.
Control Precision: Bioreactor machine has higher control precision to meet the stringent requirements of processes such as cell culture; fermenter machine is less complex and have relatively lower control precision.
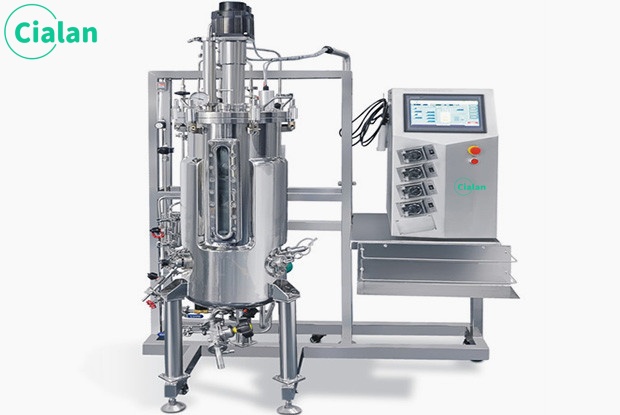

What Is Fermentation?
Fermentation process meaning is the process of chemical transformation of organic matter under anaerobic conditions through the metabolism of microorganisms. Such as alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation, acetic acid fermentation and alkaline fermentation.
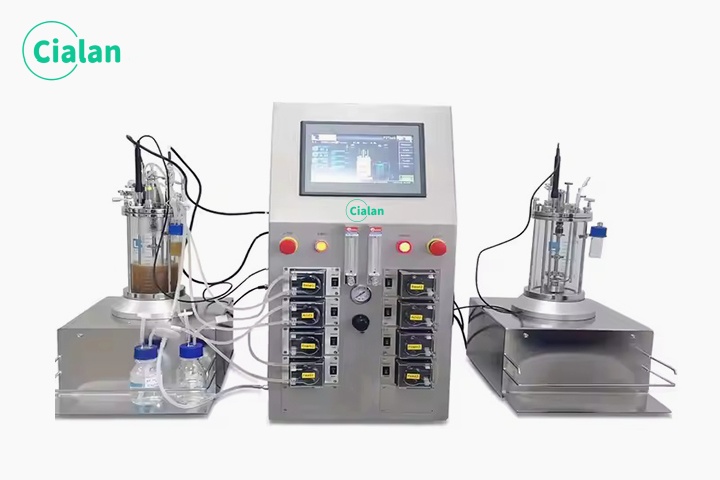

What Is The Principle Of A Bioreactor Fermenter?
The principle of a biological reactor is to provide a stable environment for the growth of cells or organisms under controlled conditions to produce a specific product.
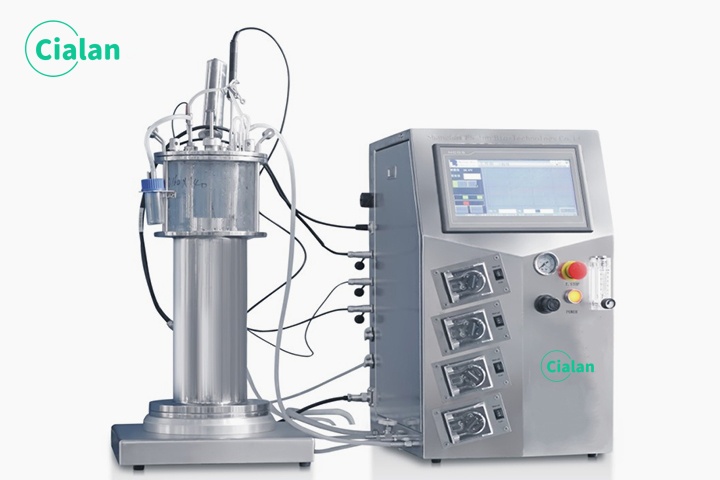

What Is The Function Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Fermenter bioreactor plays an important function in all areas of biotechnology, providing a tightly controlled environment for cell growth, bioproduct manufacturing, wastewater treatment, and the production of enzymes, antibiotics, and other drugs..
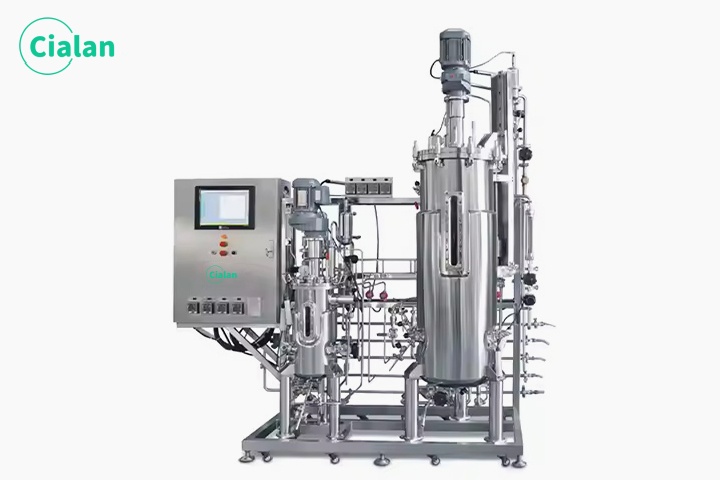

What Are The Different Types Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Material: Stainless steel bioreactor, glass bioreactor and disposable bioreactor(Polymers and plastics).
Catalyst: Enzyme bioreactor and cell bioreactor. Enzyme bioreactor includes homogeneous enzyme bioreactor, filled bed bioreactor and fluidized bed bioreactor or membrane bioreactor.
Operation mode: Batch bioreactor, continuous bioreactor and semi-continuous bioreactor.
Material mixing mode: Mechanically stirred bioreactor (Aerated mechanically stirred microbial fermenter), air-flow stirred bioreactor (Bubble column bioreactors and cyclic flow bioreactor), and airlift bioreactors.
Cell types: Microbial bioreactor, Animal cell bioreactor, and plant cell bioreactor.
Commonly, there are also photobioreactor, perfusion bioreactor, membrane bioreactor, and wave bioreactor.
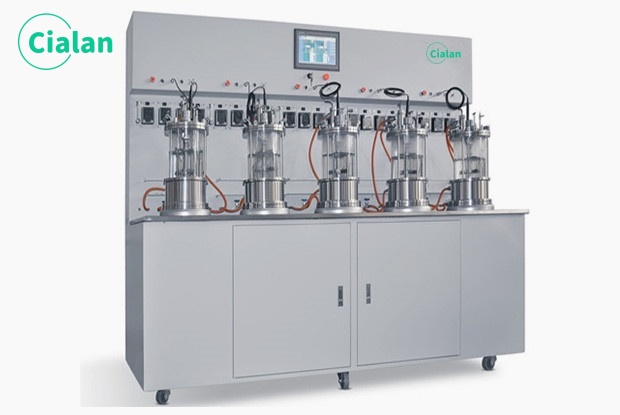

What Is The Most Commonly Used Bioreactor Fermenter?
The most commonly used bioreactor fermenter is stirred tank bioreactor (STR), with the advantages of homogeneous mixing capacity, good temperature control, high efficiency of oxygen transfer and ease of scaling up the process for mass production of biotechnology products.
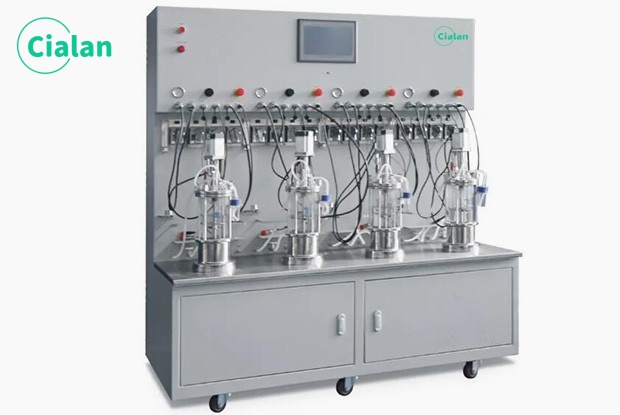

How Does A Bioreactor Fermenter Work?
Fermentors allow organisms and media to grow, reproduce and metabolize by providing a controlled environment (temperature, pH, oxygen concentration and nutrient supply).
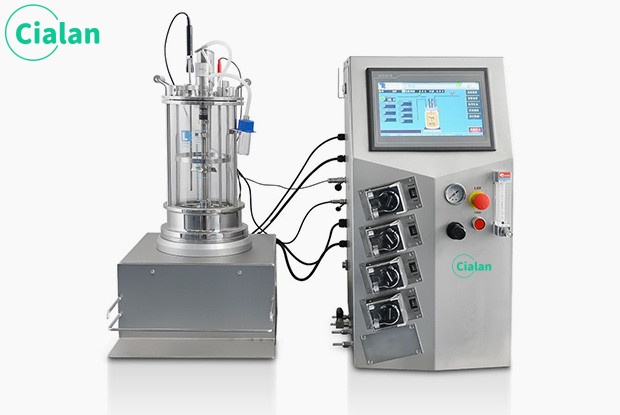

How To Control The Normal Reaction Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Aseptic environment: Preventing contamination of cultures and keeping the bioreactor running under sterile conditions for a long time are critical steps in bioreactor design.
Cell and Microbial Concentration: Microbial concentrations must be high enough throughout the bioprocess operation to achieve high yields.
Animal cells, on the other hand, need to reach a minimum density to begin growth.
Temperature: Temperature affects enzyme activity, cell growth rate, and direction of metabolism. This is controlled by temperature sensors, jackets on the bioreactor and a temperature control unit (TCU).
pH: Maintaining the correct pH in the bioreactor is important for cell metabolism and to mimic the natural environment of the cells.
DO: Optical or electrochemical dissolved oxygen probes are used to detect key limiting factors in the aerobic process.
Stirring: Effective agitation is essential to achieve efficient mixing. Distribute cultures, temperature, pH, nutrients and oxygen evenly and prevent sedimentation. Switch to air-lift reactors for shear stress sensitive cells.
Pressure: Use pressure sensors to detect and maintain a sterile environment and prevent foam overflow.
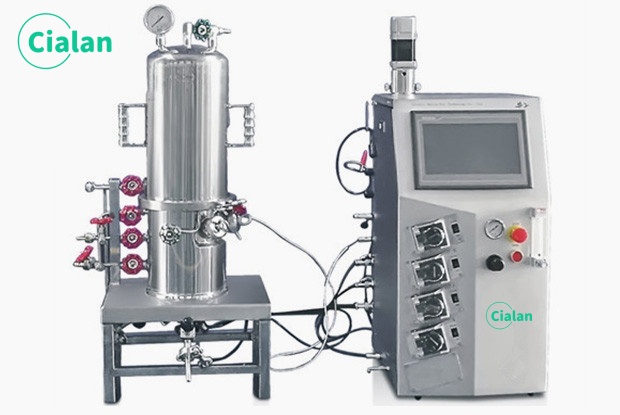

How To Control The Pressure Of Fermentation Tank?
The method of controlling pressure, generally for the adjustment of inlet or outlet valves, change the amount of air (or gas) into or out of the experimental process to maintain the required pressure. In the automatic control of the fermenter, you can choose Cialan company's manometer or a variety of remote pressure gauge, they can be converted into a variety of electrical signals and then connected to the instrument, the latter according to the size of the pressure, feedback control valve switch to achieve the purpose of regulation.
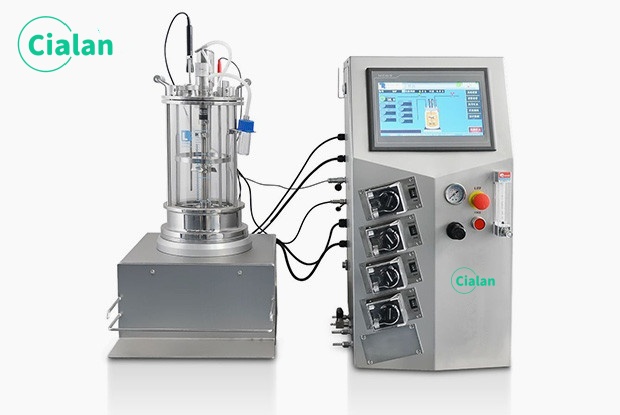

How To Control Temperature When Fermentation?
A typical approach to regulating the temperature of a bioreactor system involves utilizing a temperature control system that pumps a temperature-controlled fluid through a surrounding jacket, effectively dissipating excess heat by modulating the flow of coolant within the jacket, while continuously monitoring the culture medium's temperature via a sensor; this closed-loop system enables accurate temperature control by referencing a predetermined setpoint.
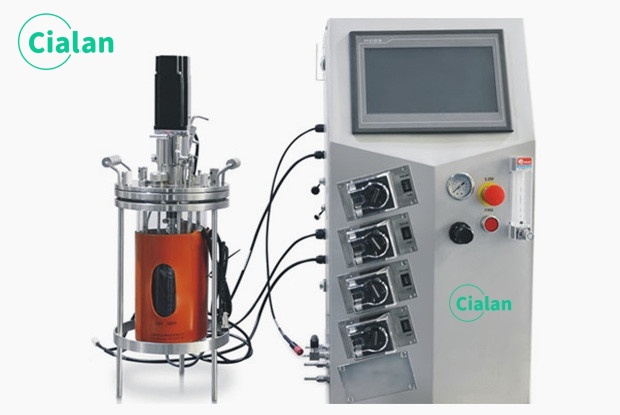

How Much Does A Bioreactor Fermenter Cost?
It wouldn't be right to mention one fixed amount.
The cost for a ferment containers will vary from model to model.
To know the exact price, you can ask your preferred manufacturer to provide a quotation for the type of bioreactor you want.
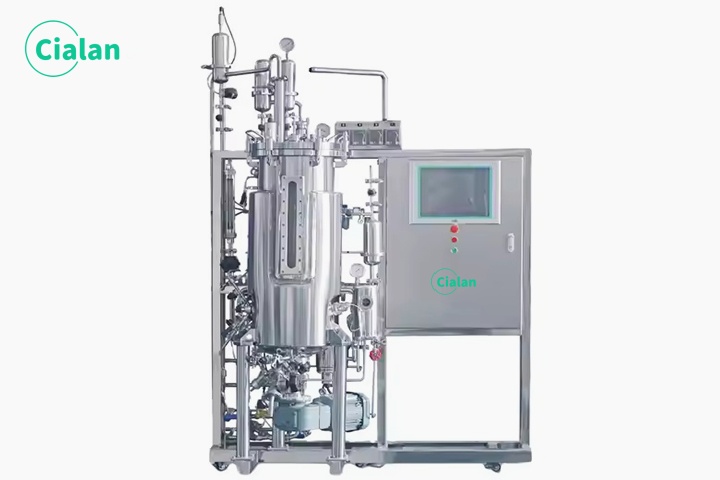

Where To Find Bioreactor Fermenter Manufacturers?
Numerous online directories can connect you with bioreactor fermenter manufacturers.
A simple search for "top-rated bioreactor fermenter manufacturers" yields multiple options. However, it's essential to exercise caution when selecting a manufacturer from online search results. Before making a decision, conduct thorough research on the company's background and reputation. Look up reviews on “Google” and reputable review sites to gauge their credibility.
Additionally, It's also crucial to review their portfolio of request that potential manufacturers share examples of their previous work to ensure they meet your standards
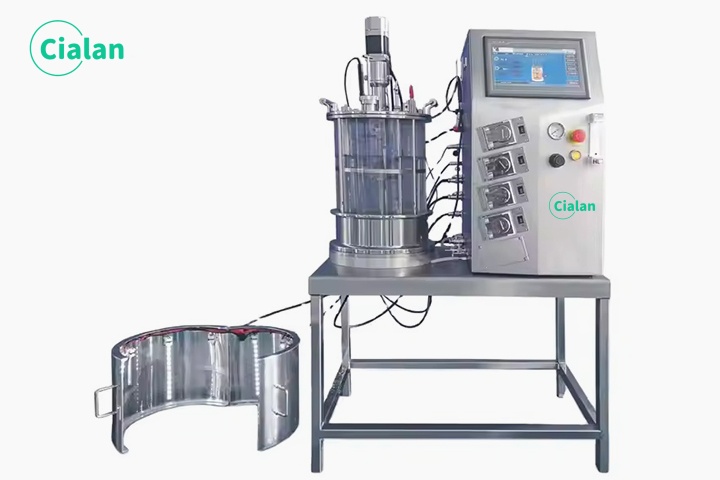

How To Choose A Right Bioreactor Fermenter System For Your Fermentation Application?
1. Application scenarios and types of organisms
Is it used to cultivate microorganisms (bacteria, yeast), animal and plant cells, enzymes, or do you need cell crushing or direct separation, batch culture, replenishment batch or continuous production?
2. Production scale
Lab scale: 1-50L benchtop bioreactor
Pilot scale-up: 50-1000L (scale-up compatibility design required).
Industrial scale: >1000L (Stainless steel stirred fermenter tank, CIP/SIP system required).
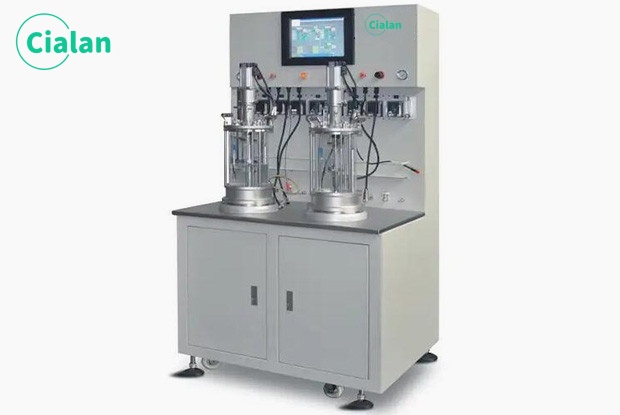

What Should You Look For In A Perfect Bioreactor Fermenter?
Size: The size of the bioreactor tanks must be consistent with the size of your research or production. Capacity sizes range from 0.5L to over 1000 liters.
Cell or organism type: Bacteria and cells have very different needs and characteristics. It is important to select a bioreactor designed specifically for the cell or organism type.
Material: The most common materials used for bioreactors are stainless steel, glass and disposable plastic. Each option has unique features
Oxygen Requirements: The gas exchange system in the bioreactor will directly affect the growth and metabolism of the organisms.
Sensor: Highly efficient and sophisticated bioreactors are equipped with sensors to monitor key parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen and nutrient supplementation in real time.
Easy to clean: The bioreactors are thoroughly cleaned and sterilized at the end of each operation.
Cost: Bioreactors should be priced to match production capacity, have low energy consumption, fewer consumables, be easy to maintain, and be easy to operate.
Supplier: A specialized bioreactor manufacturer should recommend which system is suitable for your specific needs based on the organisms you are processing and the size you want.
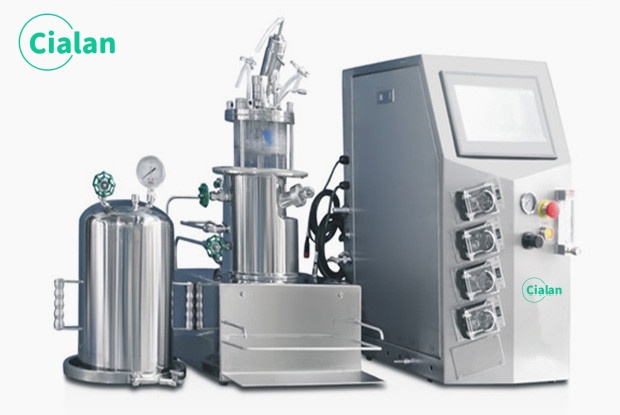

What Are Application For Bioreactor And Fermenter?
Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
Production of vaccines, antibodies, medicinal proteins, enzymes, cells cultivation, transplantation and regeneration, growth hormones, insulin, tissue engineering.
Food and Beverage
Fermentation foods such as beer, wine, yogurt, cheese, bread, fermented soy products.
Food additives such as citric acid, lactic acid, amino acids.
Various beverages.
Environmental biotechnology
Wastewater treatment: Utilizing microorganisms to degrade organic pollutants.
Exhaust gas treatment: Removal of harmful gases by microbial filtration.
Solid waste treatment: Composting and anaerobic digestion.
Research and Education
Microbial culture: For basic and applied research.
Metabolic engineering: Optimization of microbial metabolic pathways.
Bioprocess development: Optimize production processes.
Chemical industry
Biofuels: Production of ethanol, biodiesel from algae or plant waste.
Bioplastics: Biodegradable plastics polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxy fatty acid esters (PHA) made from renewable resources.
Enzymes: Amylase, protease, lipase
Agriculture
Bio-fertilizers: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria.
Biopesticides: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
Feed additives: Probiotics, enzymes.
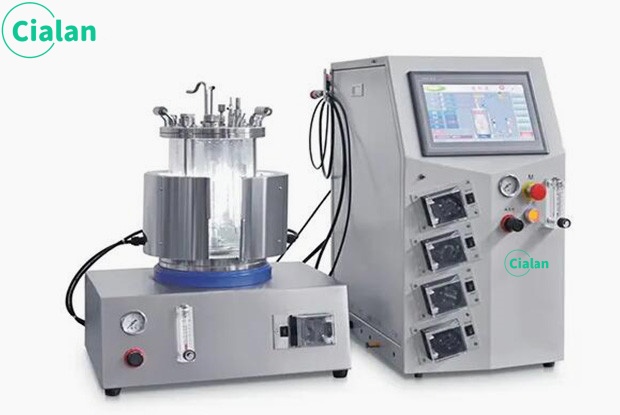

What Is The Difference Between Conical And Round Bottom Fermentation Tank?
Conical fermenter: The bottom is conical (cone angle is usually 60°-90°), the H/D ratio is usually 2:1 to 4:1. The conical bottom facilitates the yeast to settle, and the top of the tank can be designed as a dome or a flat lid. Typical industries are beer brewing (fermentation and maturation of Lagers).
Cylindrical fermenter: The main body is cylindrical, the bottom is flat or slightly curved. H/D ratio is usually 1:1 to 2:1. The internal structure is simple, no special internal components, partially equipped with stirring paddles or baffles. Typical industries are traditional brewing, dairy product fermentation.
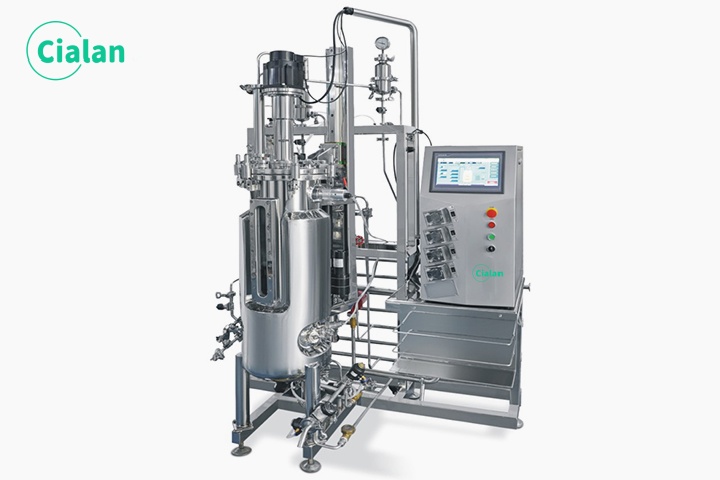

What Are The Main Components Of A Bioreactor Fermenter?
Reaction vessel: The main part, which holds the organisms (Bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells, etc.) and the culture medium. Usually made of stainless steel or glass.
Stirred tank: Mixes the medium and organisms to ensure uniform distribution of nutrients (Mechanical stirring paddles or air-lift cycles).
Baffles: Prevent the formation of vortices or rotation within the liquid during agitation. Improves the flow of the medium and prevents possible damage to microorganisms or cells.
Foam control system: Prevents excess foam from building up in the vessel causing overflow and damage to the bioreactor vessel.
Oxygen supply/aeration system: Deliver oxygen to maintain dissolved oxygen (DO). Sparger can deliver sterile air.
Temperature control system: Maintain constant temperature through jacket water circulation or electric heating.
pH Monitoring and Adjustment: Real-time monitoring through sensors and automatic addition of acid/base solution to adjust pH.
Nutrient supplementation system: Continuous or batch addition of carbon, nitrogen and other nutrients.
Gas Discharge System: Discharge exhaust gases (CO₂) produced by metabolism.
Sampling port: Inlet of the medium for easy monitoring and analysis.
Feeding port: Introduction of additional material. Sterile filters maintain a sterile and controlled environment.
Data acquisition and automation: Real-time monitoring of key parameters (Dissolved oxygen, temperature, cell density) through sensors and computers.
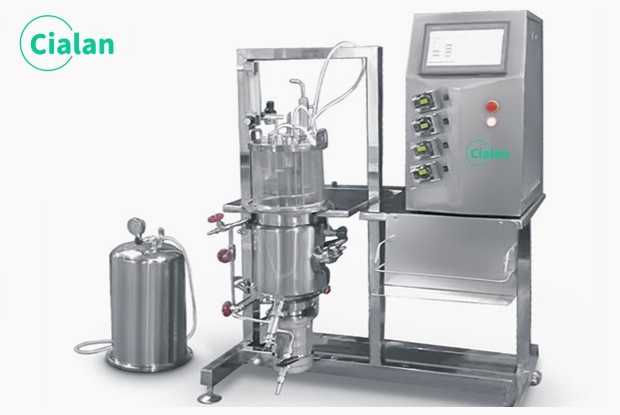

What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Advantages:
High efficiency and scale-up: high product concentration, continuous operation.
Precise environmental control: parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), nutrient supply, etc. can be monitored and adjusted in real time with high repeatability.
Wide range of applications: from pharmaceutical, food to environmental protection. Supports a wide range of biocatalytic systems such as microorganisms, plant and animal cells, and enzymes.
Environmentally friendly: Reduced chemical pollution and recyclable resources.
High flexibility: choose different types of reactors according to the needs, and support various operation modes such as batch, replenishment batch, and continuous.
Disadvantages:
High cost: expensive equipment, high energy consumption, frequent maintenance.
Technical complexity: high operational threshold, high risk of contamination .
Amplification challenges: uneven mass transfer, shear damage .
Difficult downstream processing: high cost of separation and purification.
Biological system limitations: metabolic inhibition, genetic instability.
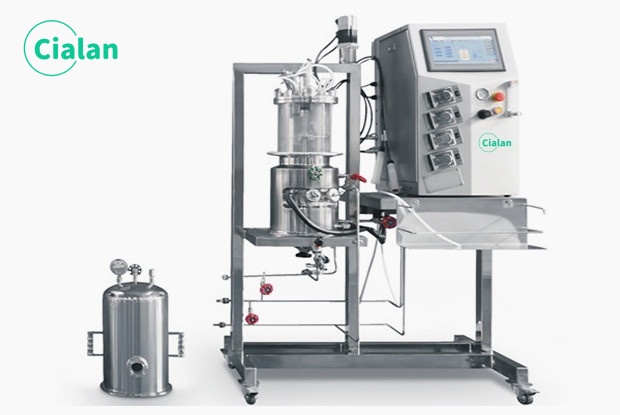

Why Should You Consider Using A Bioreactor Fermenter?
The glass fermentation jar should not be used to soak strong acids, alkalis, etc. Do not clean the fermenter with corrosive liquids to prevent corrosion and damage.
Do not touch the walls of the tank with your hands to prevent burns.
The bottom of the tank should be kept flat, and all connecting surfaces should be sealed without any leakage.
Calibrate the pH probe, dissolved oxygen electrode and temperature sensor regularly to avoid data deviation that may cause the process to go out of control.
Pay attention to the temperature control to ensure that the temperature inside the tank reaches the optimal state, to prevent the fermenter from being damaged due to high temperature. If the requirements are not met, the water should be heated or cooled to the appropriate temperature before use.
Before using the fermenter container, it must be inspected first, and if any parts are found to be loose or damaged, they should be replaced or repaired in time.
In the process of use, if you find that there are abnormalities occur, you should immediately cut off the power supply and stop using. Please notify professional maintenance personnel immediately for overhaul or replacement.
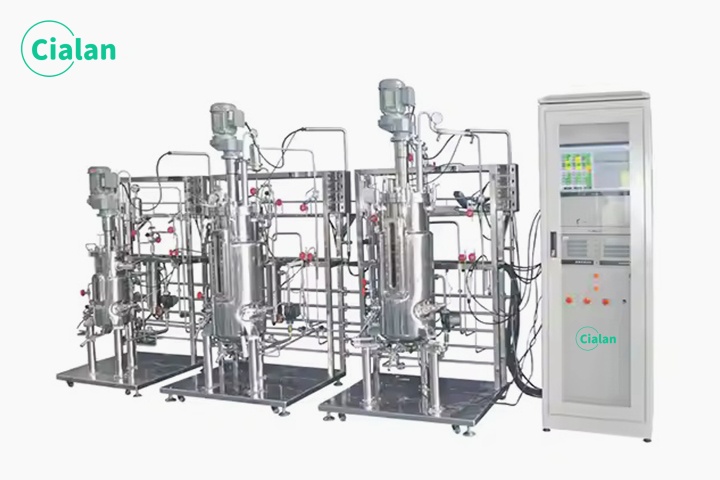

How To Clean A Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. Clean regularly with a brush or bristle brush to avoid foam residue on the surface of the fermentor.
2. Use professional cleaning solution to clean.
3. After rinsing the fermenter with water, you need to dry it with a towel in time to maintain a dry and sterile environment.
4. If there is oil or stains left, you can use neutral cleaner to clean.
5. Sterilize the fermenter regularly to ensure a hygienic environment.
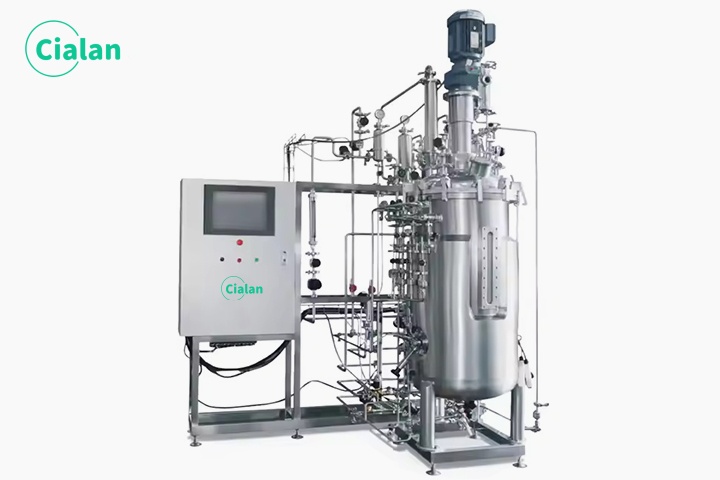

What Solution Is Used To Clean A Bioreactor Fermenter?
How To Sterilize A Bioreactor Fermenter?
Removing parts: Wrap the interfaces of the stirring motor, DO electrode and pH electrode with tin foil and wrap tightly to prevent them from falling off during the sterilizer process. Remove the defoaming cable line, air tube and other parts in turn.
Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the inner wall and parts of the reactor to remove residues.
Loading: Load the parts into the autoclave.
Sterilization parameters: 121℃, 20 minutes (the specific time is adjusted according to the loading volume).
Venting and drying: Slowly vent the liquid medium after sterilization to avoid boiling, followed by drying.
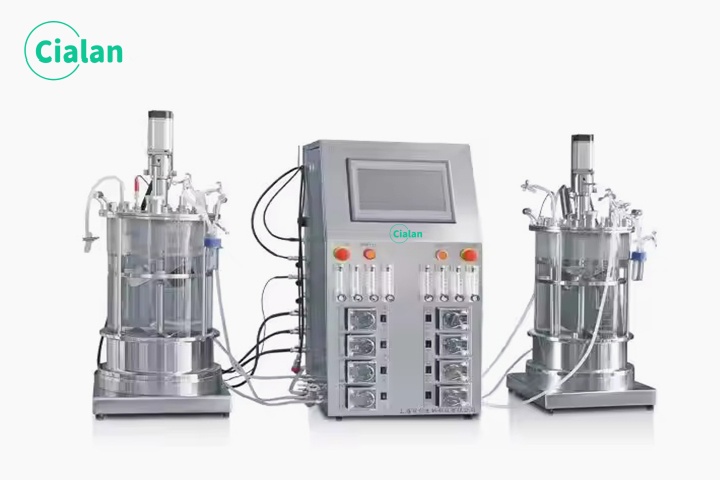

How To Place A Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. Suitable location
The plane is stable, such as anti-vibration table or fixed test bench, there is enough space for operation and maintenance, pay attention to ventilation and exhaust.
2. Environmental control
The operating environment should be constant temperature and humidity and sterile.
3. Safety requirements
Ensure biological safety, explosion-proof, fire-proof and leak-proof.
4. Supporting facilities
Water and electricity supply, equipped with UPS or backup generator in case of power failure. Convenient material in and out of the reasonable, easy to data and monitoring.
5. Regulations and Compliance
Environmental protection approval, to comply with the requirements of fire escape, load-bearing structure, etc.

Can You Customize The Bioreactor Fermenter To Our Specifications?
Yes, send us your specifics and Cialan will provide the perfect design solution for your laboratory or production.
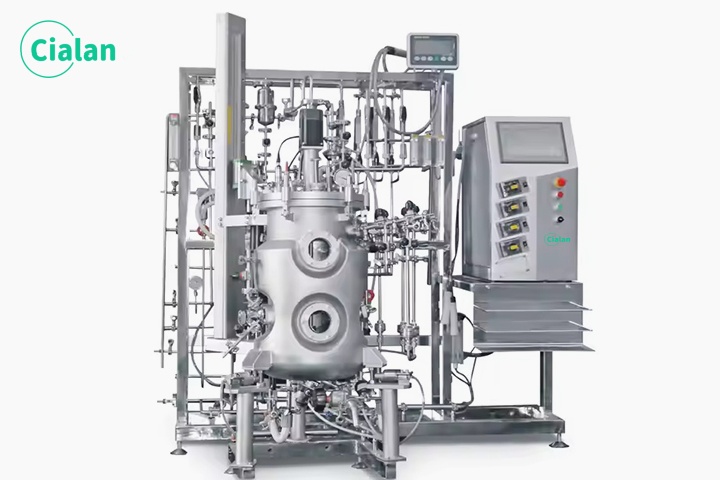

How To Do The Maintenance Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. If the inlet pipe and outlet pipe joint leakage, when tightening the joint does not solve the problem, should add or replace the packing.
2. Pressure gauge and safety valve should be inspected regularly, if there is any failure, it should be replaced or repaired in time.
3. When cleaning the bioreactor, please use a soft brush to scrub, don't scrape with a hard tool, so as not to damage the surface of the fermenter.
4. Supporting instruments should be calibrated once a year to ensure normal use.
5. Electrical appliances, meters, sensors and other electrical equipment is strictly prohibited from direct contact with water and steam to prevent moisture.
6. When the bioreactor equipment is out of use, it should be cleaned in time, exhaust the fermenter and the residual water in the pipeline; loosen the lid of the fermentation tank and the hand hole screws to prevent permanent deformation of the seal.
7. The operating platform, constant temperature water tank and other carbon steel equipment should be regularly (once a year) paint to prevent corrosion.
8. Often check the reducer oil level, such as lubricant is not enough, need to increase in a timely manner.
9. Regular replacement of reducer lubricant to extend its service life.
10. If the fermentation tank is not used for a while, it is necessary to empty the fermentor and exhaust the residual water in the tank and pipelines.

What Is The Problems And Solutions For A Bioreactor Fermenter?
(1). Temperature control fails: It could be due to a damaged temperature sensor, wire, or gauge.
Solution: Inspect the sensor and gauge, and replace them promptly if any problems are detected.
(2). Abnormal pressure occurs after closing the valve: It may be caused by loose flange screws on the tank cover, damaged sealing rings, or leaks in pipe joints or valves.
Solution: Tighten the screws and nuts, and check and replace the fermenter sealing ring if needed.
(3). Leaks can result from air intake issues or leakage, leading to sealing problems.
Solution: Tighten the fastening screws, check the fermenter sealing ring for damage, and tighten the nuts as needed.
(4). Sterilization heating speed is too slow: It could be due to low steam pressure or insufficient gas supply in the laboratory bioreactor.
Solution: Verify if the electric heating tube or other heating components of the fermenter are burnt out.
(5). Abnormal pH display: It may indicate a blocked or damaged pH electrode.
Solution: Inspect the pH electrode, clean or replace it accordingly.
(6). An abnormal DO display may be caused by a damaged dissolved oxygen electrode membrane.
Solution: Replace the membrane to address this issue.
(7). If the DO value is too low, it could be due to insufficient air intake, a clogged filter, or leaking pipeline valves in the laboratory bioreactor.
Solution: Adjust the air intake by opening the large valve, check and replace the filter element if needed, and verify the tightness of the valves.

Is There Any Warranty On Bioreactor Fermenter?
Bioreactor fermenter warranty
For optimal performance, it is important to regularly maintain your bioreactor fermenter, so it can operate efficiently for an extended period. It is essential to be aware of the warranty coverage for your equipment, as it ensures that any manufacturing issues will be repaired at no additional cost by the supplier. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase a bioreactor fermenter from a manufacturer that offers warranty services —Cialan.
Reputable amusement manufacturers typically provide a 1-year warranty. for example, offers complimentary repair and maintenance services during the first year.
Before purchasing a bioreactor, it is advisable to review the warranty period and other associated terms and conditions.

What After-Sale Service Does A Bioreactor Fermenter Provide?
Bioreactor fermenter after-sale service
The reliable bioreactor fermenter manufacturer offers the following after-sale services:
1. Secure product delivery.
2. Thorough inspection prior to installation.
3. Complimentary online guidance for device installation and maintenance.
4. Free training for your users.
5. Regular assessments of your bioreactor fermenter.

Can You Do OEM&ODM For Bioreactor Fermenter?
Yes, Cialan can do OEM/OEM for our users, just send us your requirements for bioreactor.

What Substances Can Be Fermented By A Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. Microbial fermentation
Bacteria: production of cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut, insulin, enzymes, proteases, vaccine development.
Yeast: production of alcohol, beer, wine, baker's yeast. Recombinant proteins.
Fungi: molds, edible mushrooms, actinomycetes
Antibiotics: streptomycin, erythromycin
2. Cell culture
Animal cells: including mammalian cells, insect cells.
Plant cells, medicinal plant cells,
Food additives
3. Enzymes and metabolites
Enzyme preparations: e.g. amylase, cellulase, lipase.
Secondary metabolites: antibiotics, vitamins.
Organic acids: citric acid, lactic acid.
4. Energy and Environmental Protection
Biofuels: microalgae, ethanol, biogas, biodiesel.
Environmental remediation: wastewater treatment, pollutant degradation.
5. Food and Beverage
Soy sauce, curd, natto. Probiotic beverages, fermented plant proteins.
6. Genetic Engineering and Synthetic Biology
Recombinant proteins: insulin, new crown vaccine.
Synthetic biomolecules: synthetic microorganisms to produce artemisinin, artificial meat.

What Is The Cell Density In A Bioreactor?
The cell density in a cell culture bioreactor is the number of cells or biomass per unit volume of culture solution and is a key parameter of the bioreaction process, directly affecting the efficiency of product synthesis, the rate of substrate consumption, and process stability. It indicates how many cells are growing in the bioreactor environment and producing the desired product. The control and monitoring of cell concentration needs to be optimized with respect to reactor type, culture conditions and target product characteristics.
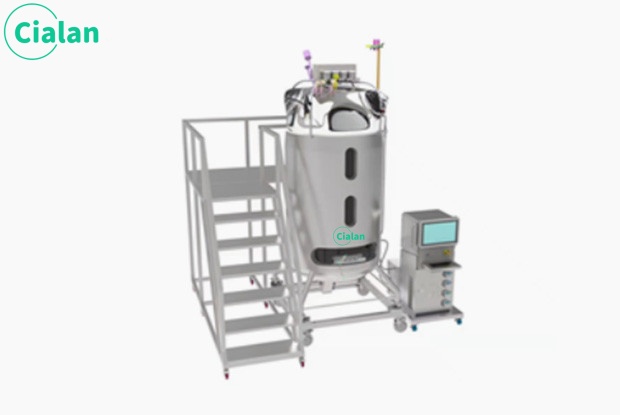

Can The Single Use Bioreactor Fermenter Be Recycled?
Single use bioreactors were originally designed for single use, with the core advantage of avoiding cross-contamination.
Their bioprocessing systems are usually made of multi-layered plastics (polyethylene,, polypropylene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers), which may not be able to withstand multiple autoclaving or chemical disinfection, and their repeated use tends to lead to deterioration of the material, rupture, or precipitation of chemicals, which is a violation of the core principles of GMP. Therefore, most disposable bioreactors are not suitable for recycling.

Which Cell Types Can Be Cultured In Bioreactor?
Laboratory bioreactor can culture many types of cells, including mammalian cells, stem cells, insect cells, bacteria, yeast, filamentous fungi, actinomycetes, plant cells, specialized cells such as microalgae and photosynthetic microorganisms. Some cells are very sensitive to shear stress, so it is important to choose the right bioreactor for cell culture.

What Causes Foaming In Bioreactor?
Agitation and Aeration
Foaming can be caused by the high speed rotation of the stirring paddles or by aeration (bubbling), as well as by the shear stresses generated by stirring.
Biological Factors
Products secreted by microorganisms and substances produced by cell lysis also generate foam.
Surface-active substances
Natural surfactants such as proteins and polysaccharides as well as an excess of antifoam agents can increase foam production.

What Is Kla And How To Calculate Kla In A Bioreactor?
In bioreactors, the volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient (KLa) is a central parameter for assessing the efficiency of oxygen transfer from the gas phase to the liquid phase, which directly affects the growth and product synthesis of aerobic microorganisms or cells. To calculate the kLa (volumetric mass transfer coefficient) in a bioreactor, dynamic venting and sensors are typically used, whereby the kLa is calculated according to a mathematical formula after a rapid reduction of the dissolved oxygen level has brought it to equilibrium;

What Is VVM And How To Calculate VVM In A Bioreactor?
By adjusting the stirrer power and the flow rate per minute per gas volume (vvm), significant energy savings can be achieved. The formula is gas flow rate (L/M)/volume of liquid (L).

What You Need To Know Before Investing In a Bioprocessing Space In Your Lab?
Prioritization of needs: Is the target of the bioprocess a cell or a microorganism, and does it require high-density cell culture, continuous fermentation, or a strictly aseptic environment?
Compliance threshold: Does it involve GMP production or highly pathogenic pathogen operations? To meet GLP and CAP.
Supporting facilities: There should be a complete ventilation system, complete utilities, and corrosion-resistant floors and walls.
Budget allocation: What is the proportion of equipment purchase, renovation, and O&M costs? Select the appropriate bioreactor according to the corresponding experimental objectives and functions. Emphasize energy consumption and consumables.
Technical support: Choose brands and suppliers with good reputation for equipment, and that can provide quick response maintenance and training services. Be 3Q certified.
Expansion space: Reserve space for new equipment, is it possible to expand or introduce new technology in the next 3-5 years?

How Do You Import A Bioreactor Fermenter From China?
Importing a bioreactor fermenter from China can be difficult for those who are new to international imports.
Purchasing from a reputable manufacturer and supplier eliminates hassle of logistics, as they handle the safe and reliable delivery of the product directly to your place.
When buying the bioreactor fermenter, it is important to keep the following points in mind:
1. Confirm that your selected supplier can securely export and deliver the machine, and ensure that your agreement includes all essential shipping information.
2. Choose the delivery way (by sea, air, or express) based on your preference.
3. Remember to factor in duty imports and taxes when calculating the total cost.

How Does a Manufacturer Deliver The Bioreactor Fermenter?
Bioreactor fermenter delivery
Safe shipping is so important as quality manufacturing.
A responsible manufacturer should deliver your bioreactor fermenter safely.
Most manufacturers use export wooden case to pack the device.
You should read all the necessary instructions available on the sides of the boxes before boxing.
In this engaging blog, we'll explore the most common questions about bioreactors such as pricing, types, maintenance, applications and principles. You'll discover how these sophisticated fermentation tank can enhance the accuracy of your bioprocessing results and increase the yield of your fermentation products.
By reading the FAQ guide, you will discover valuable advice on choosing the perfect bioreactor to match your lab or factory. In addition, we share tips on how to choose a reputable manufacturer, understand the difference between bioreactors and fermenters, how to use these products, and how to utilize these bioreactors for a more stable biological culture process.
Whether you are in a lab where cells and microorganisms are cultured or a plant where fermentation products are produced, you will find everything you need here.
Bioreactors are a central tool in the field of bioengineering, covering areas such as food, agriculture, scientific research, industrial production, healthcare, environmental protection and social sustainability. Consulting with bioreactor manufacturers and application specialists can help you decide which system is best suited for your specific needs.

What Is A Bioreactor?
BIoreactors definition in biology as a device used to culture cells or microorganisms under controlled conditions. This includes the cultivation of various types of animal, plant and human cells, as well as the fermentation of bacteria, yeast and fungi. etc.

What Is A Fermenter?
Fermenters are closed vessels specially designed for the microbial fermentation process to produce a variety of fermentation products. Such as fermentation foods, beverages, beer, Lactic acid bacteria, yeast, alcohol, dairy products etc.

What Is The Difference Between Bioreactor And Fermenter?
Application: Bioreactor tank can be used for various biological processes, including tissue engineering, mammalian cell culture, etc. While fermenter tank is mainly used for microbial fermentation, such as bacteria, yeast or fungi, and producing fermentation products, which is a kind of bioreactor.
Design and Construction: Bioreactors have more advanced and complex control systems. Often designed with specific features to meet the needs of fermenting organisms.
Size: Bioreactors can be designed in different shapes and sizes depending on the application; fermenter vessel is usually conical or cylindrical and have a larger capacity than bioreactor.
Control Precision: Bioreactor machine has higher control precision to meet the stringent requirements of processes such as cell culture; fermenter machine is less complex and have relatively lower control precision.

What Is Fermentation?
Fermentation process meaning is the process of chemical transformation of organic matter under anaerobic conditions through the metabolism of microorganisms. Such as alcoholic fermentation, lactic acid fermentation, acetic acid fermentation and alkaline fermentation.

What Is The Principle Of A Bioreactor Fermenter?
The principle of a biological reactor is to provide a stable environment for the growth of cells or organisms under controlled conditions to produce a specific product.

What Is The Function Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Fermenter bioreactor plays an important function in all areas of biotechnology, providing a tightly controlled environment for cell growth, bioproduct manufacturing, wastewater treatment, and the production of enzymes, antibiotics, and other drugs..

What Are The Different Types Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Material: Stainless steel bioreactor, glass bioreactor and disposable bioreactor(Polymers and plastics).
Catalyst: Enzyme bioreactor and cell bioreactor. Enzyme bioreactor includes homogeneous enzyme bioreactor, filled bed bioreactor and fluidized bed bioreactor or membrane bioreactor.
Operation mode: Batch bioreactor, continuous bioreactor and semi-continuous bioreactor.
Material mixing mode: Mechanically stirred bioreactor (Aerated mechanically stirred microbial fermenter), air-flow stirred bioreactor (Bubble column bioreactors and cyclic flow bioreactor), and airlift bioreactors.
Cell types: Microbial bioreactor, Animal cell bioreactor, and plant cell bioreactor.
Commonly, there are also photobioreactor, perfusion bioreactor, membrane bioreactor, and wave bioreactor.

What Is The Most Commonly Used Bioreactor Fermenter?
The most commonly used bioreactor fermenter is stirred tank bioreactor (STR), with the advantages of homogeneous mixing capacity, good temperature control, high efficiency of oxygen transfer and ease of scaling up the process for mass production of biotechnology products.

How Does A Bioreactor Fermenter Work?
Fermentors allow organisms and media to grow, reproduce and metabolize by providing a controlled environment (temperature, pH, oxygen concentration and nutrient supply).

How To Control The Normal Reaction Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Aseptic environment: Preventing contamination of cultures and keeping the bioreactor running under sterile conditions for a long time are critical steps in bioreactor design.
Cell and Microbial Concentration: Microbial concentrations must be high enough throughout the bioprocess operation to achieve high yields.
Animal cells, on the other hand, need to reach a minimum density to begin growth.
Temperature: Temperature affects enzyme activity, cell growth rate, and direction of metabolism. This is controlled by temperature sensors, jackets on the bioreactor and a temperature control unit (TCU).
pH: Maintaining the correct pH in the bioreactor is important for cell metabolism and to mimic the natural environment of the cells.
DO: Optical or electrochemical dissolved oxygen probes are used to detect key limiting factors in the aerobic process.
Stirring: Effective agitation is essential to achieve efficient mixing. Distribute cultures, temperature, pH, nutrients and oxygen evenly and prevent sedimentation. Switch to air-lift reactors for shear stress sensitive cells.
Pressure: Use pressure sensors to detect and maintain a sterile environment and prevent foam overflow.

How To Control The Pressure Of Fermentation Tank?
The method of controlling pressure, generally for the adjustment of inlet or outlet valves, change the amount of air (or gas) into or out of the experimental process to maintain the required pressure. In the automatic control of the fermenter, you can choose Cialan company's manometer or a variety of remote pressure gauge, they can be converted into a variety of electrical signals and then connected to the instrument, the latter according to the size of the pressure, feedback control valve switch to achieve the purpose of regulation.

How To Control Temperature When Fermentation?
A typical approach to regulating the temperature of a bioreactor system involves utilizing a temperature control system that pumps a temperature-controlled fluid through a surrounding jacket, effectively dissipating excess heat by modulating the flow of coolant within the jacket, while continuously monitoring the culture medium's temperature via a sensor; this closed-loop system enables accurate temperature control by referencing a predetermined setpoint.

How Much Does A Bioreactor Fermenter Cost?
It wouldn't be right to mention one fixed amount.
The cost for a ferment containers will vary from model to model.
To know the exact price, you can ask your preferred manufacturer to provide a quotation for the type of bioreactor you want.

Where To Find Bioreactor Fermenter Manufacturers?
Numerous online directories can connect you with bioreactor fermenter manufacturers.
A simple search for "top-rated bioreactor fermenter manufacturers" yields multiple options. However, it's essential to exercise caution when selecting a manufacturer from online search results. Before making a decision, conduct thorough research on the company's background and reputation. Look up reviews on “Google” and reputable review sites to gauge their credibility.
Additionally, It's also crucial to review their portfolio of request that potential manufacturers share examples of their previous work to ensure they meet your standards

How To Choose A Right Bioreactor Fermenter System For Your Fermentation Application?
1. Application scenarios and types of organisms
Is it used to cultivate microorganisms (bacteria, yeast), animal and plant cells, enzymes, or do you need cell crushing or direct separation, batch culture, replenishment batch or continuous production?
2. Production scale
Lab scale: 1-50L benchtop bioreactor
Pilot scale-up: 50-1000L (scale-up compatibility design required).
Industrial scale: >1000L (Stainless steel stirred fermenter tank, CIP/SIP system required).

What Should You Look For In A Perfect Bioreactor Fermenter?
Size: The size of the bioreactor tanks must be consistent with the size of your research or production. Capacity sizes range from 0.5L to over 1000 liters.
Cell or organism type: Bacteria and cells have very different needs and characteristics. It is important to select a bioreactor designed specifically for the cell or organism type.
Material: The most common materials used for bioreactors are stainless steel, glass and disposable plastic. Each option has unique features
Oxygen Requirements: The gas exchange system in the bioreactor will directly affect the growth and metabolism of the organisms.
Sensor: Highly efficient and sophisticated bioreactors are equipped with sensors to monitor key parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen and nutrient supplementation in real time.
Easy to clean: The bioreactors are thoroughly cleaned and sterilized at the end of each operation.
Cost: Bioreactors should be priced to match production capacity, have low energy consumption, fewer consumables, be easy to maintain, and be easy to operate.
Supplier: A specialized bioreactor manufacturer should recommend which system is suitable for your specific needs based on the organisms you are processing and the size you want.

What Are Application For Bioreactor And Fermenter?
Medicine and Pharmaceuticals
Production of vaccines, antibodies, medicinal proteins, enzymes, cells cultivation, transplantation and regeneration, growth hormones, insulin, tissue engineering.
Food and Beverage
Fermentation foods such as beer, wine, yogurt, cheese, bread, fermented soy products.
Food additives such as citric acid, lactic acid, amino acids.
Various beverages.
Environmental biotechnology
Wastewater treatment: Utilizing microorganisms to degrade organic pollutants.
Exhaust gas treatment: Removal of harmful gases by microbial filtration.
Solid waste treatment: Composting and anaerobic digestion.
Research and Education
Microbial culture: For basic and applied research.
Metabolic engineering: Optimization of microbial metabolic pathways.
Bioprocess development: Optimize production processes.
Chemical industry
Biofuels: Production of ethanol, biodiesel from algae or plant waste.
Bioplastics: Biodegradable plastics polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxy fatty acid esters (PHA) made from renewable resources.
Enzymes: Amylase, protease, lipase
Agriculture
Bio-fertilizers: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria.
Biopesticides: Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt).
Feed additives: Probiotics, enzymes.

What Is The Difference Between Conical And Round Bottom Fermentation Tank?
Conical fermenter: The bottom is conical (cone angle is usually 60°-90°), the H/D ratio is usually 2:1 to 4:1. The conical bottom facilitates the yeast to settle, and the top of the tank can be designed as a dome or a flat lid. Typical industries are beer brewing (fermentation and maturation of Lagers).
Cylindrical fermenter: The main body is cylindrical, the bottom is flat or slightly curved. H/D ratio is usually 1:1 to 2:1. The internal structure is simple, no special internal components, partially equipped with stirring paddles or baffles. Typical industries are traditional brewing, dairy product fermentation.

What Are The Main Components Of A Bioreactor Fermenter?
Reaction vessel: The main part, which holds the organisms (Bacteria, yeast, mammalian cells, etc.) and the culture medium. Usually made of stainless steel or glass.
Stirred tank: Mixes the medium and organisms to ensure uniform distribution of nutrients (Mechanical stirring paddles or air-lift cycles).
Baffles: Prevent the formation of vortices or rotation within the liquid during agitation. Improves the flow of the medium and prevents possible damage to microorganisms or cells.
Foam control system: Prevents excess foam from building up in the vessel causing overflow and damage to the bioreactor vessel.
Oxygen supply/aeration system: Deliver oxygen to maintain dissolved oxygen (DO). Sparger can deliver sterile air.
Temperature control system: Maintain constant temperature through jacket water circulation or electric heating.
pH Monitoring and Adjustment: Real-time monitoring through sensors and automatic addition of acid/base solution to adjust pH.
Nutrient supplementation system: Continuous or batch addition of carbon, nitrogen and other nutrients.
Gas Discharge System: Discharge exhaust gases (CO₂) produced by metabolism.
Sampling port: Inlet of the medium for easy monitoring and analysis.
Feeding port: Introduction of additional material. Sterile filters maintain a sterile and controlled environment.
Data acquisition and automation: Real-time monitoring of key parameters (Dissolved oxygen, temperature, cell density) through sensors and computers.

What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
Advantages:
High efficiency and scale-up: high product concentration, continuous operation.
Precise environmental control: parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), nutrient supply, etc. can be monitored and adjusted in real time with high repeatability.
Wide range of applications: from pharmaceutical, food to environmental protection. Supports a wide range of biocatalytic systems such as microorganisms, plant and animal cells, and enzymes.
Environmentally friendly: Reduced chemical pollution and recyclable resources.
High flexibility: choose different types of reactors according to the needs, and support various operation modes such as batch, replenishment batch, and continuous.
Disadvantages:
High cost: expensive equipment, high energy consumption, frequent maintenance.
Technical complexity: high operational threshold, high risk of contamination .
Amplification challenges: uneven mass transfer, shear damage .
Difficult downstream processing: high cost of separation and purification.
Biological system limitations: metabolic inhibition, genetic instability.

Why Should You Consider Using A Bioreactor Fermenter?
The glass fermentation jar should not be used to soak strong acids, alkalis, etc. Do not clean the fermenter with corrosive liquids to prevent corrosion and damage.
Do not touch the walls of the tank with your hands to prevent burns.
The bottom of the tank should be kept flat, and all connecting surfaces should be sealed without any leakage.
Calibrate the pH probe, dissolved oxygen electrode and temperature sensor regularly to avoid data deviation that may cause the process to go out of control.
Pay attention to the temperature control to ensure that the temperature inside the tank reaches the optimal state, to prevent the fermenter from being damaged due to high temperature. If the requirements are not met, the water should be heated or cooled to the appropriate temperature before use.
Before using the fermenter container, it must be inspected first, and if any parts are found to be loose or damaged, they should be replaced or repaired in time.
In the process of use, if you find that there are abnormalities occur, you should immediately cut off the power supply and stop using. Please notify professional maintenance personnel immediately for overhaul or replacement.

How To Clean A Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. Clean regularly with a brush or bristle brush to avoid foam residue on the surface of the fermentor.
2. Use professional cleaning solution to clean.
3. After rinsing the fermenter with water, you need to dry it with a towel in time to maintain a dry and sterile environment.
4. If there is oil or stains left, you can use neutral cleaner to clean.
5. Sterilize the fermenter regularly to ensure a hygienic environment.

What Solution Is Used To Clean A Bioreactor Fermenter?
| Residue Type | Recommended Cleaning Solution |
| Proteins | 1-2% NaOH solution (alkaline) |
| Lipids/oils | 1-3% HNO₃ or neutral detergent (acidic) |
| Inorganic salt scale | 5-10% citric acid or EDTA solution |
| Biofilm | Disinfectant containing peracetic acid or sodium hypochlorite |

How To Sterilize A Bioreactor Fermenter?
Removing parts: Wrap the interfaces of the stirring motor, DO electrode and pH electrode with tin foil and wrap tightly to prevent them from falling off during the sterilizer process. Remove the defoaming cable line, air tube and other parts in turn.
Cleaning: Thoroughly clean the inner wall and parts of the reactor to remove residues.
Loading: Load the parts into the autoclave.
Sterilization parameters: 121℃, 20 minutes (the specific time is adjusted according to the loading volume).
Venting and drying: Slowly vent the liquid medium after sterilization to avoid boiling, followed by drying.

How To Place A Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. Suitable location
The plane is stable, such as anti-vibration table or fixed test bench, there is enough space for operation and maintenance, pay attention to ventilation and exhaust.
2. Environmental control
The operating environment should be constant temperature and humidity and sterile.
3. Safety requirements
Ensure biological safety, explosion-proof, fire-proof and leak-proof.
4. Supporting facilities
Water and electricity supply, equipped with UPS or backup generator in case of power failure. Convenient material in and out of the reasonable, easy to data and monitoring.
5. Regulations and Compliance
Environmental protection approval, to comply with the requirements of fire escape, load-bearing structure, etc.

Can You Customize The Bioreactor Fermenter To Our Specifications?
Yes, send us your specifics and Cialan will provide the perfect design solution for your laboratory or production.

How To Do The Maintenance Of Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. If the inlet pipe and outlet pipe joint leakage, when tightening the joint does not solve the problem, should add or replace the packing.
2. Pressure gauge and safety valve should be inspected regularly, if there is any failure, it should be replaced or repaired in time.
3. When cleaning the bioreactor, please use a soft brush to scrub, don't scrape with a hard tool, so as not to damage the surface of the fermenter.
4. Supporting instruments should be calibrated once a year to ensure normal use.
5. Electrical appliances, meters, sensors and other electrical equipment is strictly prohibited from direct contact with water and steam to prevent moisture.
6. When the bioreactor equipment is out of use, it should be cleaned in time, exhaust the fermenter and the residual water in the pipeline; loosen the lid of the fermentation tank and the hand hole screws to prevent permanent deformation of the seal.
7. The operating platform, constant temperature water tank and other carbon steel equipment should be regularly (once a year) paint to prevent corrosion.
8. Often check the reducer oil level, such as lubricant is not enough, need to increase in a timely manner.
9. Regular replacement of reducer lubricant to extend its service life.
10. If the fermentation tank is not used for a while, it is necessary to empty the fermentor and exhaust the residual water in the tank and pipelines.

What Is The Problems And Solutions For A Bioreactor Fermenter?
(1). Temperature control fails: It could be due to a damaged temperature sensor, wire, or gauge.
Solution: Inspect the sensor and gauge, and replace them promptly if any problems are detected.
(2). Abnormal pressure occurs after closing the valve: It may be caused by loose flange screws on the tank cover, damaged sealing rings, or leaks in pipe joints or valves.
Solution: Tighten the screws and nuts, and check and replace the fermenter sealing ring if needed.
(3). Leaks can result from air intake issues or leakage, leading to sealing problems.
Solution: Tighten the fastening screws, check the fermenter sealing ring for damage, and tighten the nuts as needed.
(4). Sterilization heating speed is too slow: It could be due to low steam pressure or insufficient gas supply in the laboratory bioreactor.
Solution: Verify if the electric heating tube or other heating components of the fermenter are burnt out.
(5). Abnormal pH display: It may indicate a blocked or damaged pH electrode.
Solution: Inspect the pH electrode, clean or replace it accordingly.
(6). An abnormal DO display may be caused by a damaged dissolved oxygen electrode membrane.
Solution: Replace the membrane to address this issue.
(7). If the DO value is too low, it could be due to insufficient air intake, a clogged filter, or leaking pipeline valves in the laboratory bioreactor.
Solution: Adjust the air intake by opening the large valve, check and replace the filter element if needed, and verify the tightness of the valves.

Is There Any Warranty On Bioreactor Fermenter?
Bioreactor fermenter warranty
For optimal performance, it is important to regularly maintain your bioreactor fermenter, so it can operate efficiently for an extended period. It is essential to be aware of the warranty coverage for your equipment, as it ensures that any manufacturing issues will be repaired at no additional cost by the supplier. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase a bioreactor fermenter from a manufacturer that offers warranty services —Cialan.
Reputable amusement manufacturers typically provide a 1-year warranty. for example, offers complimentary repair and maintenance services during the first year.
Before purchasing a bioreactor, it is advisable to review the warranty period and other associated terms and conditions.

What After-Sale Service Does A Bioreactor Fermenter Provide?
Bioreactor fermenter after-sale service
The reliable bioreactor fermenter manufacturer offers the following after-sale services:
1. Secure product delivery.
2. Thorough inspection prior to installation.
3. Complimentary online guidance for device installation and maintenance.
4. Free training for your users.
5. Regular assessments of your bioreactor fermenter.

Can You Do OEM&ODM For Bioreactor Fermenter?
Yes, Cialan can do OEM/OEM for our users, just send us your requirements for bioreactor.

What Substances Can Be Fermented By A Bioreactor Fermenter?
1. Microbial fermentation
Bacteria: production of cheese, yogurt, sauerkraut, insulin, enzymes, proteases, vaccine development.
Yeast: production of alcohol, beer, wine, baker's yeast. Recombinant proteins.
Fungi: molds, edible mushrooms, actinomycetes
Antibiotics: streptomycin, erythromycin
2. Cell culture
Animal cells: including mammalian cells, insect cells.
Plant cells, medicinal plant cells,
Food additives
3. Enzymes and metabolites
Enzyme preparations: e.g. amylase, cellulase, lipase.
Secondary metabolites: antibiotics, vitamins.
Organic acids: citric acid, lactic acid.
4. Energy and Environmental Protection
Biofuels: microalgae, ethanol, biogas, biodiesel.
Environmental remediation: wastewater treatment, pollutant degradation.
5. Food and Beverage
Soy sauce, curd, natto. Probiotic beverages, fermented plant proteins.
6. Genetic Engineering and Synthetic Biology
Recombinant proteins: insulin, new crown vaccine.
Synthetic biomolecules: synthetic microorganisms to produce artemisinin, artificial meat.

What Is The Cell Density In A Bioreactor?
The cell density in a cell culture bioreactor is the number of cells or biomass per unit volume of culture solution and is a key parameter of the bioreaction process, directly affecting the efficiency of product synthesis, the rate of substrate consumption, and process stability. It indicates how many cells are growing in the bioreactor environment and producing the desired product. The control and monitoring of cell concentration needs to be optimized with respect to reactor type, culture conditions and target product characteristics.

Can The Single Use Bioreactor Fermenter Be Recycled?
Single use bioreactors were originally designed for single use, with the core advantage of avoiding cross-contamination.
Their bioprocessing systems are usually made of multi-layered plastics (polyethylene,, polypropylene, ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers), which may not be able to withstand multiple autoclaving or chemical disinfection, and their repeated use tends to lead to deterioration of the material, rupture, or precipitation of chemicals, which is a violation of the core principles of GMP. Therefore, most disposable bioreactors are not suitable for recycling.

Which Cell Types Can Be Cultured In Bioreactor?
Laboratory bioreactor can culture many types of cells, including mammalian cells, stem cells, insect cells, bacteria, yeast, filamentous fungi, actinomycetes, plant cells, specialized cells such as microalgae and photosynthetic microorganisms. Some cells are very sensitive to shear stress, so it is important to choose the right bioreactor for cell culture.

What Causes Foaming In Bioreactor?
Agitation and Aeration
Foaming can be caused by the high speed rotation of the stirring paddles or by aeration (bubbling), as well as by the shear stresses generated by stirring.
Biological Factors
Products secreted by microorganisms and substances produced by cell lysis also generate foam.
Surface-active substances
Natural surfactants such as proteins and polysaccharides as well as an excess of antifoam agents can increase foam production.

What Is Kla And How To Calculate Kla In A Bioreactor?
In bioreactors, the volumetric oxygen transfer coefficient (KLa) is a central parameter for assessing the efficiency of oxygen transfer from the gas phase to the liquid phase, which directly affects the growth and product synthesis of aerobic microorganisms or cells. To calculate the kLa (volumetric mass transfer coefficient) in a bioreactor, dynamic venting and sensors are typically used, whereby the kLa is calculated according to a mathematical formula after a rapid reduction of the dissolved oxygen level has brought it to equilibrium;

What Is VVM And How To Calculate VVM In A Bioreactor?
By adjusting the stirrer power and the flow rate per minute per gas volume (vvm), significant energy savings can be achieved. The formula is gas flow rate (L/M)/volume of liquid (L).

What You Need To Know Before Investing In a Bioprocessing Space In Your Lab?
Prioritization of needs: Is the target of the bioprocess a cell or a microorganism, and does it require high-density cell culture, continuous fermentation, or a strictly aseptic environment?
Compliance threshold: Does it involve GMP production or highly pathogenic pathogen operations? To meet GLP and CAP.
Supporting facilities: There should be a complete ventilation system, complete utilities, and corrosion-resistant floors and walls.
Budget allocation: What is the proportion of equipment purchase, renovation, and O&M costs? Select the appropriate bioreactor according to the corresponding experimental objectives and functions. Emphasize energy consumption and consumables.
Technical support: Choose brands and suppliers with good reputation for equipment, and that can provide quick response maintenance and training services. Be 3Q certified.
Expansion space: Reserve space for new equipment, is it possible to expand or introduce new technology in the next 3-5 years?

How Do You Import A Bioreactor Fermenter From China?
Importing a bioreactor fermenter from China can be difficult for those who are new to international imports.
Purchasing from a reputable manufacturer and supplier eliminates hassle of logistics, as they handle the safe and reliable delivery of the product directly to your place.
When buying the bioreactor fermenter, it is important to keep the following points in mind:
1. Confirm that your selected supplier can securely export and deliver the machine, and ensure that your agreement includes all essential shipping information.
2. Choose the delivery way (by sea, air, or express) based on your preference.
3. Remember to factor in duty imports and taxes when calculating the total cost.

How Does a Manufacturer Deliver The Bioreactor Fermenter?
Bioreactor fermenter delivery
Safe shipping is so important as quality manufacturing.
A responsible manufacturer should deliver your bioreactor fermenter safely.
Most manufacturers use export wooden case to pack the device.
You should read all the necessary instructions available on the sides of the boxes before boxing.