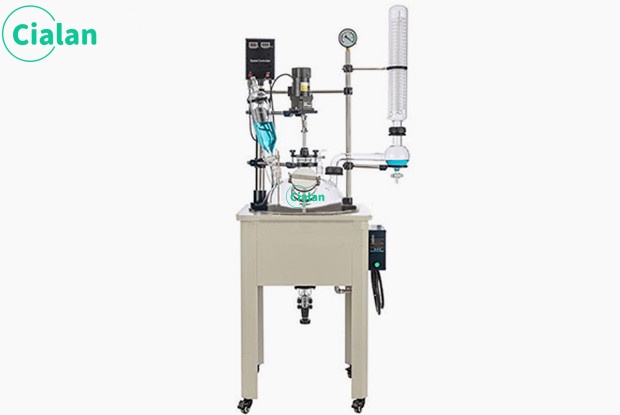
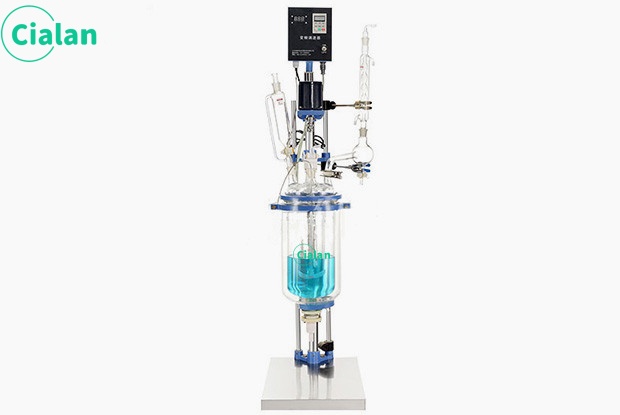
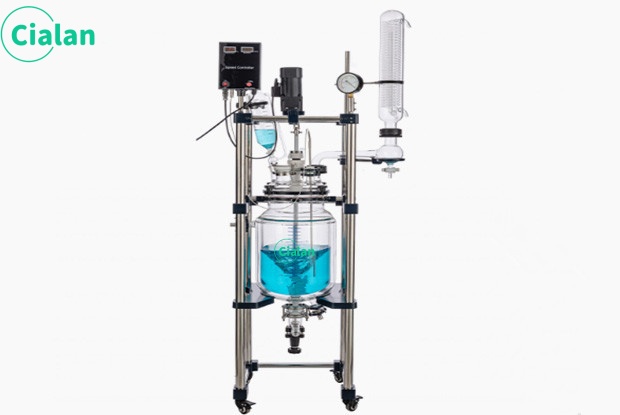
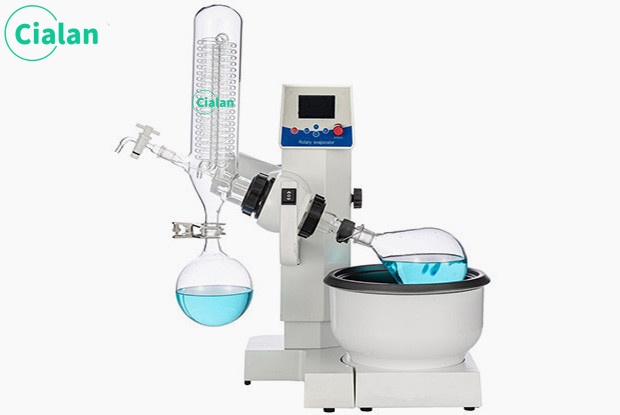
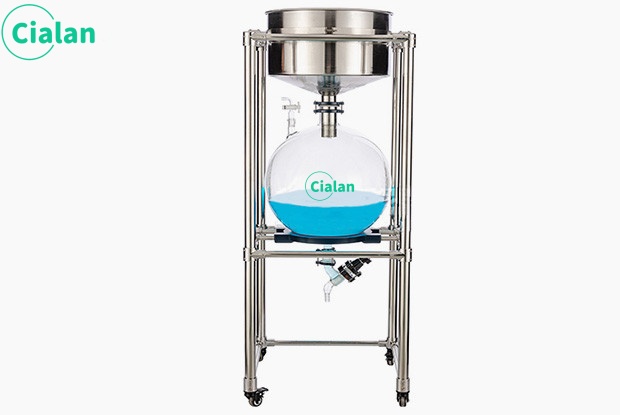
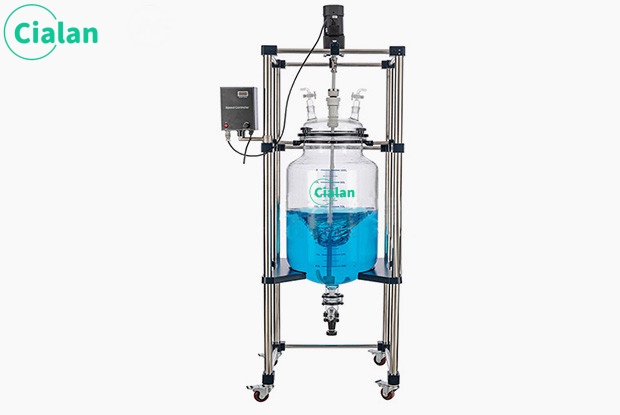
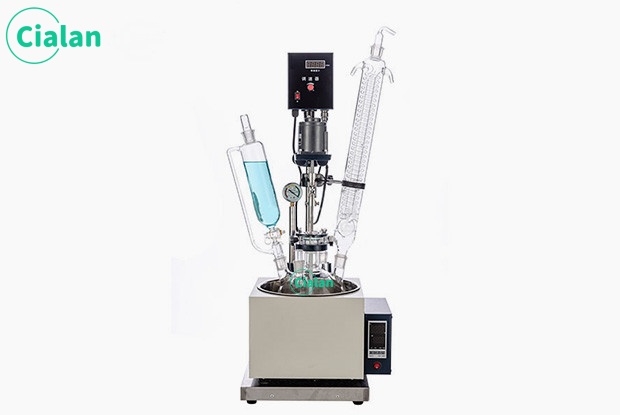
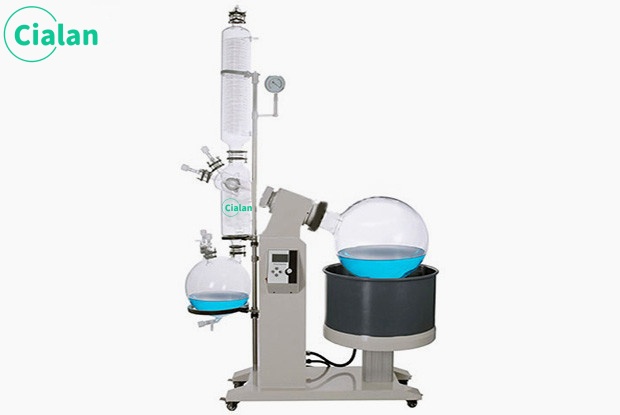
Glass separator extractor is an important tool in chemistry experiments.
Glass separator extractor: An important tool in chemistry experiments.
The glass separator extractor is an indispensable tool in chemical experiments. Its main function is to separate and collect two or more immiscible liquids. The design principles and operating methods of this instrument are of great significance to ensure the accuracy and safety of the experiment.
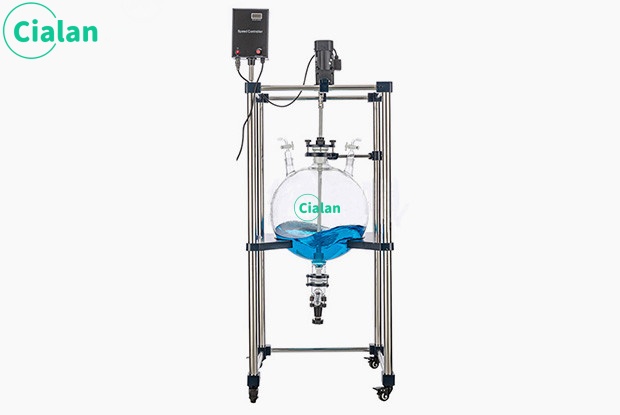

1. Glass separator extractor structure:
The instrument mainly consists of two parts: separatory funnel and receiving bottle. A separatory funnel is a glass container with a spherical or pear-shaped lower part equipped with a tight ground stopper and an outlet tube at the lower part. The receiving bottle is a glass bottle that matches the separatory funnel and is used to collect the liquid separated in the separatory funnel.
2. Working principle of glass separator extractor:
The working principle of glass dispensers is based on the difference in specific gravity and viscosity between liquids. When two or more liquids are mixed together, the liquid with greater specific gravity will sink and the liquid with less specific gravity will rise. The separatory funnel separates the mixed liquid at multiple levels, so that different liquids are collected into receiving bottles at the outlet tube.
3. Operation method of glass separator extractor:
When using this instrument, you first need to pour the liquid to be separated into a separatory funnel, and then shake it gently to mix the liquid. Next, buckle the receiving bottle tightly onto the outlet tube of the separatory funnel and wait for the liquid to separate. When different layers of liquids gather at the outlet tube, rotate the stopper of the receiving bottle so that one layer of liquid flows into the receiving bottle. Repeat this process until all the liquid to be separated has been collected into the receiving bottle.
4. Application of glass separator extractor in chemical experiments:
This instrument is widely used in various scenarios where liquid mixtures need to be separated in chemical experiments. For example, in organic chemistry experiments, this instrument is often needed to separate organic solvents and water; in analytical chemistry experiments, it can be used to separate and collect different components in samples; in addition, it is also widely used in biochemistry and in environmental chemistry experiments.
5. Precautions for using glass separator extractor:
When using this instrument, you need to pay attention to the following points: First, make sure that the instrument is clean and dry to avoid affecting the experimental results; second, handle it with care when operating to avoid breaking the instrument; in addition, you need to check whether the instrument is intact before use to avoid accidents. Safety accident; finally, clean it in time and store it properly after use.
In short, as an important tool in chemical experiments, glass dispensers play an irreplaceable role. Mastering its structure, principles, operating methods and precautions will help improve the accuracy and safety of experiments.
The glass separator extractor is an indispensable tool in chemical experiments. Its main function is to separate and collect two or more immiscible liquids. The design principles and operating methods of this instrument are of great significance to ensure the accuracy and safety of the experiment.

1. Glass separator extractor structure:
The instrument mainly consists of two parts: separatory funnel and receiving bottle. A separatory funnel is a glass container with a spherical or pear-shaped lower part equipped with a tight ground stopper and an outlet tube at the lower part. The receiving bottle is a glass bottle that matches the separatory funnel and is used to collect the liquid separated in the separatory funnel.
2. Working principle of glass separator extractor:
The working principle of glass dispensers is based on the difference in specific gravity and viscosity between liquids. When two or more liquids are mixed together, the liquid with greater specific gravity will sink and the liquid with less specific gravity will rise. The separatory funnel separates the mixed liquid at multiple levels, so that different liquids are collected into receiving bottles at the outlet tube.
3. Operation method of glass separator extractor:
When using this instrument, you first need to pour the liquid to be separated into a separatory funnel, and then shake it gently to mix the liquid. Next, buckle the receiving bottle tightly onto the outlet tube of the separatory funnel and wait for the liquid to separate. When different layers of liquids gather at the outlet tube, rotate the stopper of the receiving bottle so that one layer of liquid flows into the receiving bottle. Repeat this process until all the liquid to be separated has been collected into the receiving bottle.
4. Application of glass separator extractor in chemical experiments:
This instrument is widely used in various scenarios where liquid mixtures need to be separated in chemical experiments. For example, in organic chemistry experiments, this instrument is often needed to separate organic solvents and water; in analytical chemistry experiments, it can be used to separate and collect different components in samples; in addition, it is also widely used in biochemistry and in environmental chemistry experiments.
5. Precautions for using glass separator extractor:
When using this instrument, you need to pay attention to the following points: First, make sure that the instrument is clean and dry to avoid affecting the experimental results; second, handle it with care when operating to avoid breaking the instrument; in addition, you need to check whether the instrument is intact before use to avoid accidents. Safety accident; finally, clean it in time and store it properly after use.
In short, as an important tool in chemical experiments, glass dispensers play an irreplaceable role. Mastering its structure, principles, operating methods and precautions will help improve the accuracy and safety of experiments.