How does a molecular distillation device work?
How does a Molecular distillation work?
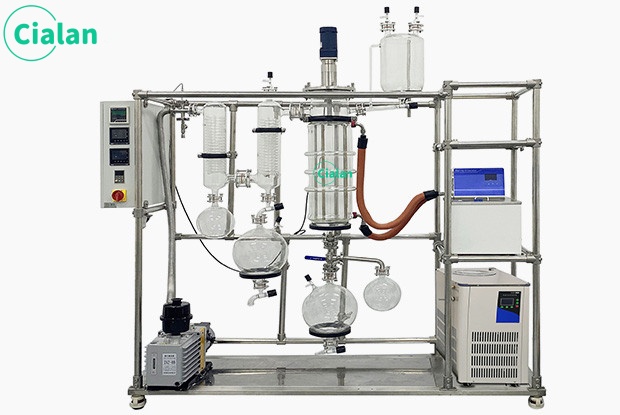
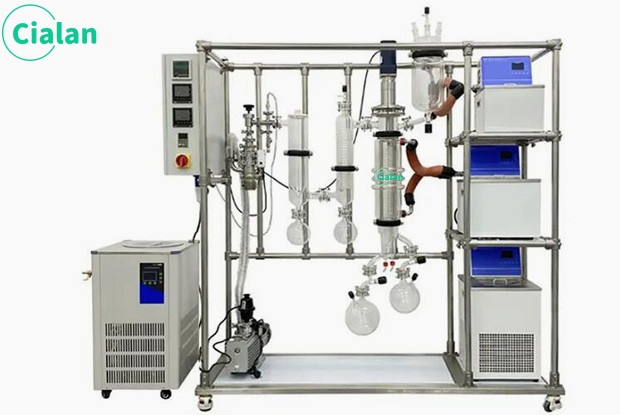
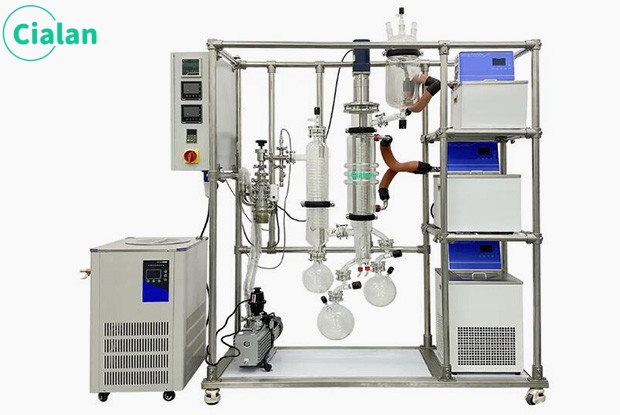
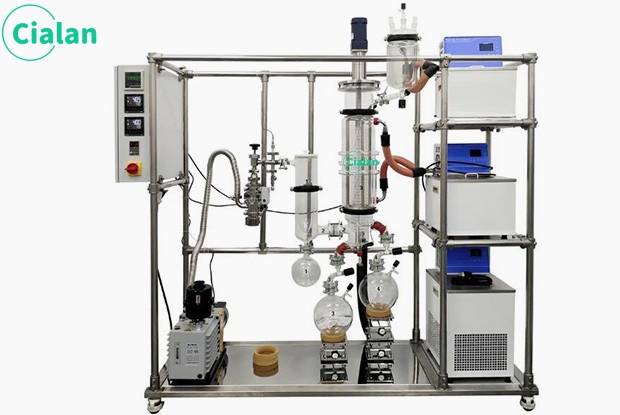
The molecular distillation experimental device is a high-efficiency evaporation and distillation equipment that uses a scraper system to force liquid into a film for evaporation or distillation. It can also perform unit operations such as deodorization, defoaming reactions, heating, and cooling. It can be widely used in medium and Western pharmaceutical, food, light industry, petroleum, chemical, environmental protection and other industries. The system can also be used in processes for recovering organic solvents from industrial waste liquids.
Method of molecular distillation.
Molecular distillation technology is a method of separation and purification by controlling the difference in boiling points of substances. In molecular distillation, substances are evaporated by heating, and the evaporated material is cooled and condensed in a condenser to separate different components. This technology mainly takes advantage of the large differences in boiling points of different substances, allowing each component to evaporate and condense separately, thereby achieving the purpose of separation and purification.
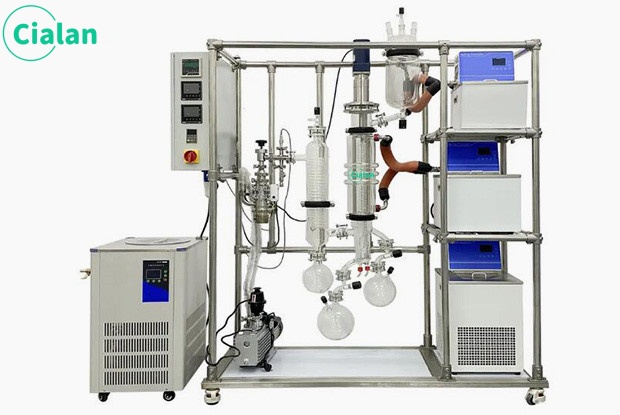

Working process of molecular distillation.
1.1. Diffusion of molecules from the main liquid phase to the evaporation surface: Usually the diffusion rate in the liquid phase is the main factor controlling the molecular distillation rate, so the thickness of the liquid layer should be reduced as much as possible and the flow of the liquid layer should be strengthened.
2. Free evaporation of molecules on the surface of the liquid layer: The evaporation rate increases with the increase of temperature, but the separation factor sometimes decreases with the increase of temperature. Therefore, the thermal stability of the material to be processed should be the premise , choose an economical and reasonable distillation temperature.
3. Molecules fly from the evaporation surface to the condensation surface: When the vapor molecules fly from the evaporation surface to the condensation surface, they may collide with each other or with the air molecules remaining between the two surfaces. Since evaporation molecules are much heavier than air molecules and most of them have the same direction of motion, their own collisions have little effect on the flying direction and evaporation speed. The residual gas molecules are in a chaotic thermal motion state between the two sides, so the number of residual gas molecules is the main factor affecting the direction of flight and evaporation speed.
4. Molecules condense on the condensation surface: As long as there is sufficient temperature difference between the hot and cold surfaces (generally 70~100℃), and the form of the condensation surface is reasonable and smooth, the condensation step can be completed in an instant.
The molecular distillation experimental device is a high-efficiency evaporation and distillation equipment that uses a scraper system to force liquid into a film for evaporation or distillation. It can also perform unit operations such as deodorization, defoaming reactions, heating, and cooling. It can be widely used in medium and Western pharmaceutical, food, light industry, petroleum, chemical, environmental protection and other industries. The system can also be used in processes for recovering organic solvents from industrial waste liquids.
Method of molecular distillation.
Molecular distillation technology is a method of separation and purification by controlling the difference in boiling points of substances. In molecular distillation, substances are evaporated by heating, and the evaporated material is cooled and condensed in a condenser to separate different components. This technology mainly takes advantage of the large differences in boiling points of different substances, allowing each component to evaporate and condense separately, thereby achieving the purpose of separation and purification.

Working process of molecular distillation.
1.1. Diffusion of molecules from the main liquid phase to the evaporation surface: Usually the diffusion rate in the liquid phase is the main factor controlling the molecular distillation rate, so the thickness of the liquid layer should be reduced as much as possible and the flow of the liquid layer should be strengthened.
2. Free evaporation of molecules on the surface of the liquid layer: The evaporation rate increases with the increase of temperature, but the separation factor sometimes decreases with the increase of temperature. Therefore, the thermal stability of the material to be processed should be the premise , choose an economical and reasonable distillation temperature.
3. Molecules fly from the evaporation surface to the condensation surface: When the vapor molecules fly from the evaporation surface to the condensation surface, they may collide with each other or with the air molecules remaining between the two surfaces. Since evaporation molecules are much heavier than air molecules and most of them have the same direction of motion, their own collisions have little effect on the flying direction and evaporation speed. The residual gas molecules are in a chaotic thermal motion state between the two sides, so the number of residual gas molecules is the main factor affecting the direction of flight and evaporation speed.
4. Molecules condense on the condensation surface: As long as there is sufficient temperature difference between the hot and cold surfaces (generally 70~100℃), and the form of the condensation surface is reasonable and smooth, the condensation step can be completed in an instant.