How to storage the blood correctly?
Introduce
The correct storage of blood is an important link and key control point to ensure the quality and safety of blood. The following are the requirements for blood storage:
1.Temperature requirements
Whole blood and red blood cells
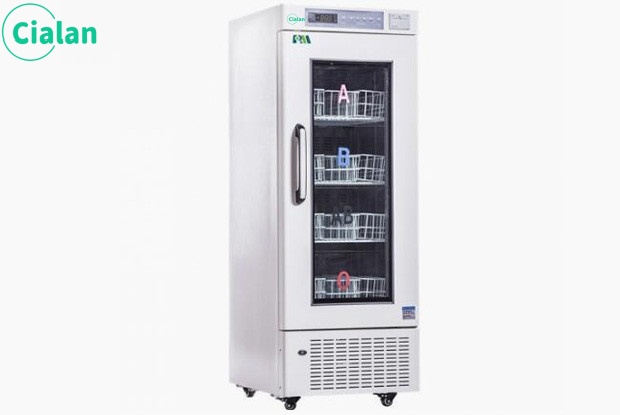
The storage temperature of whole blood and red blood cells is generally 2℃ to 6℃. Within this temperature range, the activity and quality of blood can be better maintained. Because within this temperature range, the metabolism of red blood cells can be slowed down, the consumption rate of glucose in the blood can be reduced, and the biological activity of red blood cells can be maintained to the greatest extent; secondly, the low temperature environment can inhibit the growth of bacteria and reduce blood contamination. Too high a temperature may cause bacterial growth and affect blood quality; too low a temperature may cause damage to blood cells.
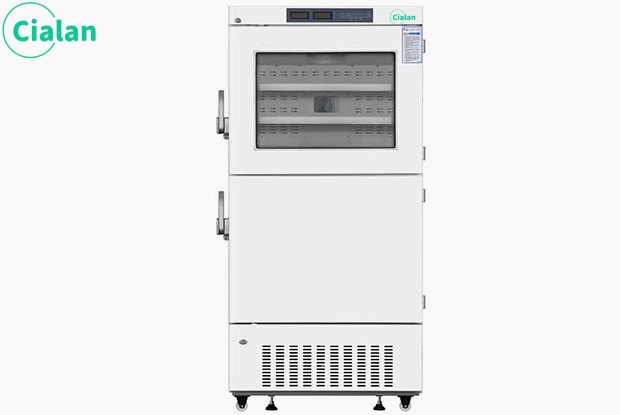
4℃ Blood Bank Refrigerator
1) Air-cooled internal circulation, uniform temperature without dead corners
2) Standard printer, data traceability
3) Designed for different blood bag sizes to improve space utilization
4) Dual temperature sensing box
Accurately detect storage temperature Selection: 1008L/608L/368L/208L/108L

Platelets
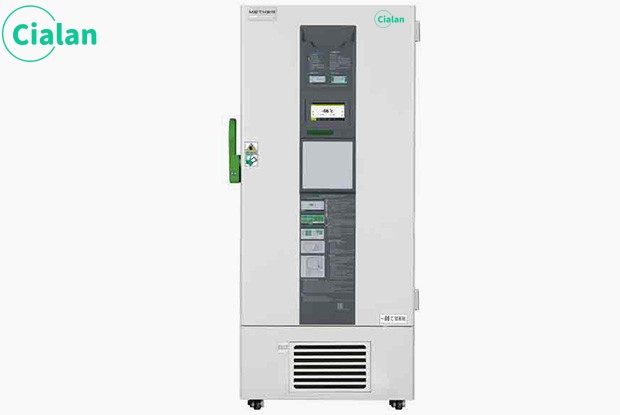
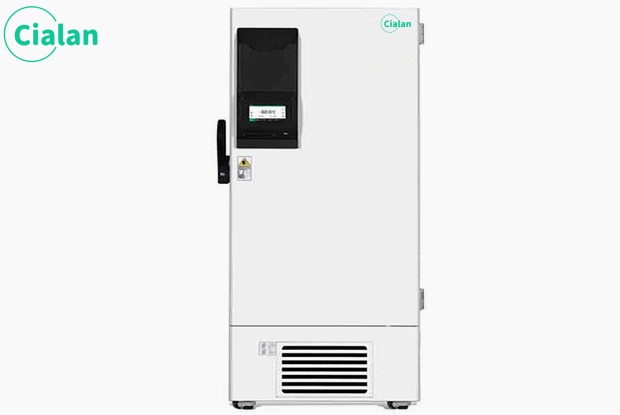
The storage temperature requirement for platelets is relatively high, generally 20℃ to 24℃. Continuous gentle oscillation. This is because storage at this temperature can maintain the integrity and activity of platelet morphology to the greatest extent, and gentle oscillation is to prevent platelet aggregation. Blood stations usually use platelet agitators and built-in incubators to maintain this temperature.
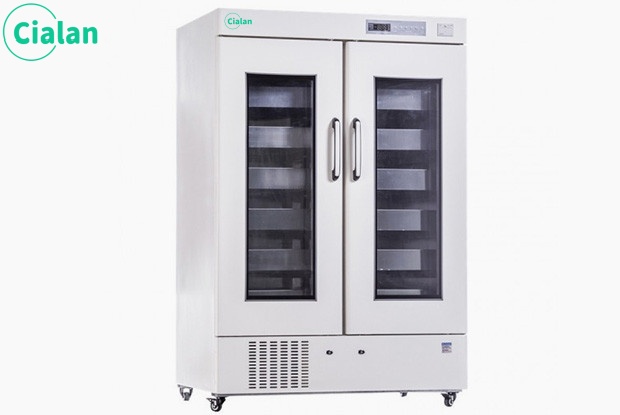
22°C platelet constant temperature storage incubator
①) Imported slide rails and motors, quiet and stable
2) UV sterilization, thermal printing
3) Real-time display of operating status
4) High-density foam insulation layer, constant temperature oscillation
Recommended selection: 10L/5L

Plasma
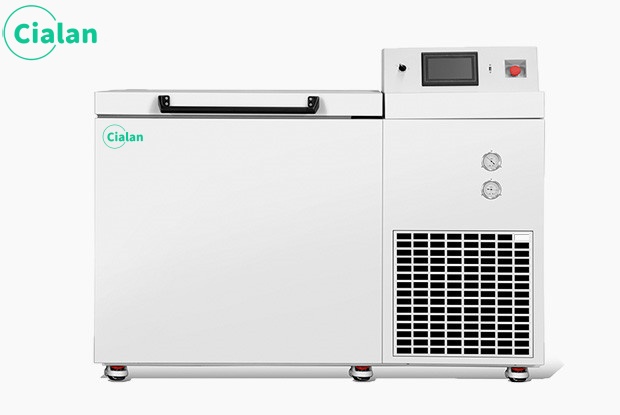
There are also specific requirements for the storage temperature of plasma. Plasma blood mainly includes fresh frozen blood, plasma frozen plasma, cold precipitated coagulation factors, etc. Plasma component blood needs to be frozen and stored at a storage temperature of ≤18°C.
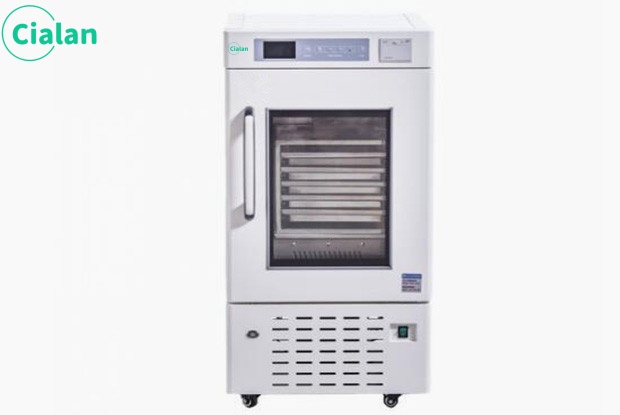
25°C low temperature biomedical storage freezer
①) Double chamber pressure relief handle design, pressure relief when the door is opened
2) Dual display and dual control, accurate and reliable
3) Data export, information can be traced back for 10 years
4) Dual chamber and dual temperature zone adjustable
Selection recommendation: 358L/528L

2. Storage facilities and equipment requirements
In blood storage, if the blood storage area needs to store blood continuously for ≥24h, there should be dual power supply or emergency power generation equipment to ensure that suitable storage conditions can be maintained in emergencies.
The storage space should meet the requirements of cleanliness, hygiene and isolation, and have fire prevention, anti-theft, anti-rat and other safety facilities. A clean and hygienic environment can reduce the risk of blood contamination, while safety facilities can ensure the safe storage of blood.
There should be sufficient lighting sources, reasonable zoning, and clear and unambiguous markings. This is convenient for staff to operate and manage, and it can also ensure that the required blood products can be found quickly and accurately.
The storage equipment should have temperature ultrasound, light alarm and 24-hour continuous temperature monitoring electronic records.
This can detect temperature abnormalities in time so that appropriate measures can be taken to ensure that the blood is always at an appropriate storage temperature.
3. Transport container requirements
When blood is transported from the collection point to the blood bank, a specific transport container is required. The purpose of the transport container is to provide a safe, temperature-controlled environment for blood and blood components so that they can maintain quality during transportation. Generally speaking, the transport container should be able to ensure that the blood is at an appropriate temperature during the transportation time of 8 to 24 hours.
For blood collected from donors at a distant collection point, a temperature-sensitive indicator such as Safe-T-Vue should be attached to monitor the temperature during transportation.
4. Documentation requirements
During the transportation of blood, documentation should be attached to identify blood components. Documentation should include important information such as donor information, blood component type, collection time, and transportation time.
In the blood bank, the storage of blood also needs to be recorded, including blood type, bottle number, expiration date, etc. When blood is issued, detailed information such as the patient's blood type, blood cross-matching date, and whether the blood is used should be recorded.
5. Quality inspection requirements
After receiving whole blood from the collection point, the blood should be checked for signs of hemolysis and the integrity of the blood bag before it can be stored in the refrigerator.
During the preparation of fresh frozen plasma, different storage conditions and preparation time will affect the quality of plasma. For example, after 2h 2-10℃ pre-storage and transportation treatment, it is placed in a 4℃ low-temperature water bath and then placed in a 2-6℃ refrigerator for storage, and the preparation is completed within 18h, which can guarantee the quality and qualified rate of plasma to the greatest extent.
Summarize
In short, the storage of blood needs to strictly follow various requirements, from temperature control, storage facilities and equipment, transportation containers, document records to quality inspection and other aspects to ensure the quality and safety of blood and provide reliable protection for clinical blood use.

The correct storage of blood is an important link and key control point to ensure the quality and safety of blood. The following are the requirements for blood storage:
1.Temperature requirements
Whole blood and red blood cells
The storage temperature of whole blood and red blood cells is generally 2℃ to 6℃. Within this temperature range, the activity and quality of blood can be better maintained. Because within this temperature range, the metabolism of red blood cells can be slowed down, the consumption rate of glucose in the blood can be reduced, and the biological activity of red blood cells can be maintained to the greatest extent; secondly, the low temperature environment can inhibit the growth of bacteria and reduce blood contamination. Too high a temperature may cause bacterial growth and affect blood quality; too low a temperature may cause damage to blood cells.
4℃ Blood Bank Refrigerator
1) Air-cooled internal circulation, uniform temperature without dead corners
2) Standard printer, data traceability
3) Designed for different blood bag sizes to improve space utilization
4) Dual temperature sensing box
Accurately detect storage temperature Selection: 1008L/608L/368L/208L/108L

Platelets
The storage temperature requirement for platelets is relatively high, generally 20℃ to 24℃. Continuous gentle oscillation. This is because storage at this temperature can maintain the integrity and activity of platelet morphology to the greatest extent, and gentle oscillation is to prevent platelet aggregation. Blood stations usually use platelet agitators and built-in incubators to maintain this temperature.
22°C platelet constant temperature storage incubator
①) Imported slide rails and motors, quiet and stable
2) UV sterilization, thermal printing
3) Real-time display of operating status
4) High-density foam insulation layer, constant temperature oscillation
Recommended selection: 10L/5L

Plasma
There are also specific requirements for the storage temperature of plasma. Plasma blood mainly includes fresh frozen blood, plasma frozen plasma, cold precipitated coagulation factors, etc. Plasma component blood needs to be frozen and stored at a storage temperature of ≤18°C.
25°C low temperature biomedical storage freezer
①) Double chamber pressure relief handle design, pressure relief when the door is opened
2) Dual display and dual control, accurate and reliable
3) Data export, information can be traced back for 10 years
4) Dual chamber and dual temperature zone adjustable
Selection recommendation: 358L/528L

2. Storage facilities and equipment requirements
In blood storage, if the blood storage area needs to store blood continuously for ≥24h, there should be dual power supply or emergency power generation equipment to ensure that suitable storage conditions can be maintained in emergencies.
The storage space should meet the requirements of cleanliness, hygiene and isolation, and have fire prevention, anti-theft, anti-rat and other safety facilities. A clean and hygienic environment can reduce the risk of blood contamination, while safety facilities can ensure the safe storage of blood.
There should be sufficient lighting sources, reasonable zoning, and clear and unambiguous markings. This is convenient for staff to operate and manage, and it can also ensure that the required blood products can be found quickly and accurately.
The storage equipment should have temperature ultrasound, light alarm and 24-hour continuous temperature monitoring electronic records.
This can detect temperature abnormalities in time so that appropriate measures can be taken to ensure that the blood is always at an appropriate storage temperature.
3. Transport container requirements
When blood is transported from the collection point to the blood bank, a specific transport container is required. The purpose of the transport container is to provide a safe, temperature-controlled environment for blood and blood components so that they can maintain quality during transportation. Generally speaking, the transport container should be able to ensure that the blood is at an appropriate temperature during the transportation time of 8 to 24 hours.
For blood collected from donors at a distant collection point, a temperature-sensitive indicator such as Safe-T-Vue should be attached to monitor the temperature during transportation.
4. Documentation requirements
During the transportation of blood, documentation should be attached to identify blood components. Documentation should include important information such as donor information, blood component type, collection time, and transportation time.
In the blood bank, the storage of blood also needs to be recorded, including blood type, bottle number, expiration date, etc. When blood is issued, detailed information such as the patient's blood type, blood cross-matching date, and whether the blood is used should be recorded.
5. Quality inspection requirements
After receiving whole blood from the collection point, the blood should be checked for signs of hemolysis and the integrity of the blood bag before it can be stored in the refrigerator.
During the preparation of fresh frozen plasma, different storage conditions and preparation time will affect the quality of plasma. For example, after 2h 2-10℃ pre-storage and transportation treatment, it is placed in a 4℃ low-temperature water bath and then placed in a 2-6℃ refrigerator for storage, and the preparation is completed within 18h, which can guarantee the quality and qualified rate of plasma to the greatest extent.
Summarize
In short, the storage of blood needs to strictly follow various requirements, from temperature control, storage facilities and equipment, transportation containers, document records to quality inspection and other aspects to ensure the quality and safety of blood and provide reliable protection for clinical blood use.