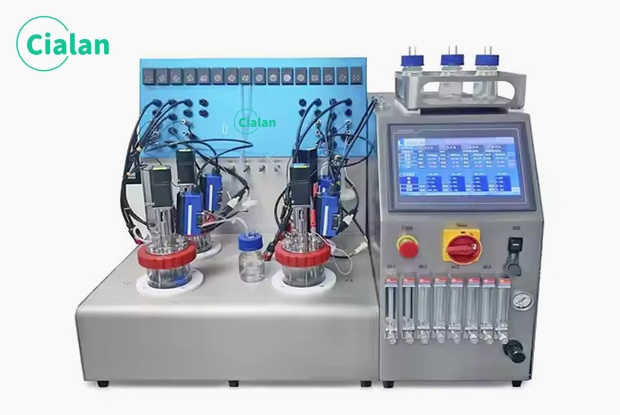
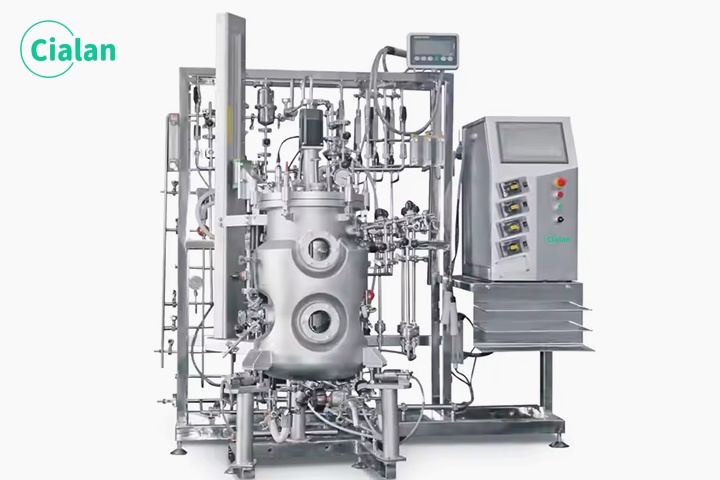
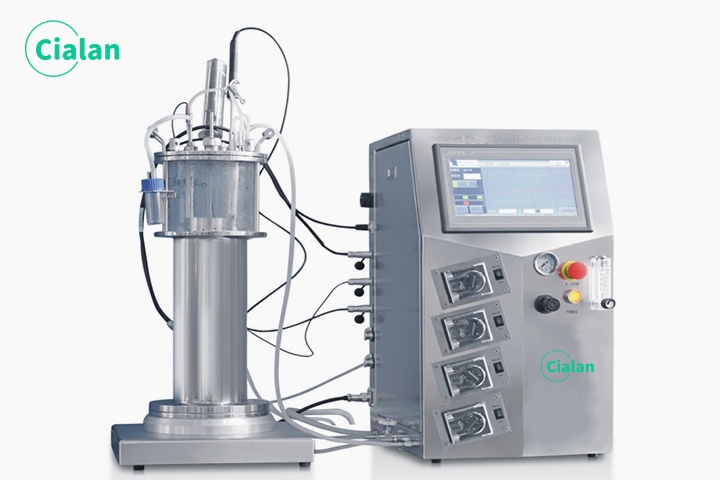
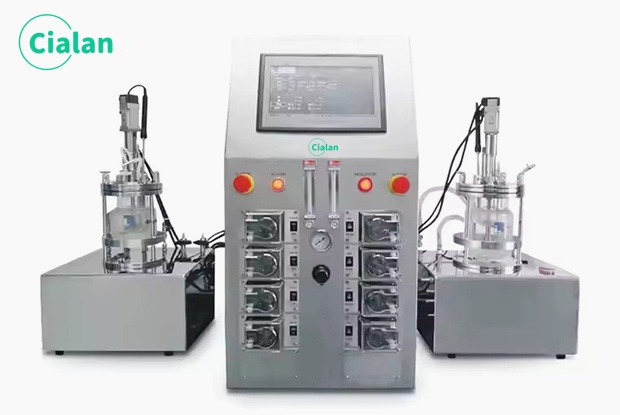
Cialan fermentation tank: Problems in organic fertilizer fermentation.
Cialan fermentation tank: Five common problems in organic fertilizer fermentation.

With the development of ecological agriculture, many farmers choose to ferment organic fertilizers independently. However, due to factors such as insufficient technical knowledge and improper selection of strains, various problems such as clumping, odor, and mosquito and fly breeding are prone to occur.
Q :
Slow heating: the pile does not heat up or heats up slowly.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.The raw materials are too wet: add dry materials according to the material ratio and then stir and ferment.
2.The raw materials are too dry: According to the humidity, add water or wet materials to maintain the moisture at 45%-55%.
3.Insufficient nitrogen source: Add ammonium sulfate with high nitrogen content to maintain the carbon-nitrogen ratio at 20:1.
4.The pile is too small, or the weather is too cold: Pile the pile high and add easily degradable substances, such as corn stalks.
5.Do not add lime or plant ash to the pile or fermentation materials. Lime or plant ash has a bactericidal effect.
Q :
The pile temperature is too high: the pile temperature is ≥65 during the fermentation process.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.Poor air permeability: Turn the pile regularly to increase the air permeability of the fermentation pile.
2.The pile is too large: reduce the size of the pile.
Q :
Odor: There is a constant smell of rotten eggs or rotten smell coming from the pile.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.The ammonia content is too high (C/N less than 20): Use microbial deodorizer for disinfection and deodorization, and add high-carbon substances, such as crop straw, peanut shells, rice husks, etc.
2.Uneven ventilation or poor air flow: remix the materials and change the formula.
3.The materials are stacked too densely: remix the pile and add large particles as appropriate according to the density of the materials.
4.Anaerobic environment: Turn the pile regularly to increase the oxygen content in the pile.
Q :
Mosquitoes and flies breed: Mosquitoes and flies breed in the fermentation pile.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.The raw materials are stacked for too long before fermentation: Process the raw materials quickly and spray microbial deodorant on the surface to reduce odor and mosquitoes.
2. Fresh feces cover the surface of the pile and breeds mosquitoes and flies: turn the pile every 2-3 days.
Q :
Material agglomeration: The material in the pile has large parts and inconsistent structure.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.Uneven mixing of raw materials or insufficient turning of piles: Improve the initial mixing method.
2.Uneven air flow or insufficient surroundings: sort or crush compost to improve air distribution.
3.The raw materials contain large pieces and non-degradable or slow-degrading materials: sort the compost, crush and organize the raw materials.
4.The composting process is not over: extend the fermentation time or improve the fermentation conditions.
Conclusion
In short, don’t worry if there are problems during the fermentation of organic fertilizer. First, find out the cause of the problem, and then find a suitable solution based on the cause of the problem and solve it as soon as possible. If the cause of the problem cannot be analyzed, do not deal with it blindly. You can consult an organic fertilizer fermentation expert and handle it according to the expert's guidance.

With the development of ecological agriculture, many farmers choose to ferment organic fertilizers independently. However, due to factors such as insufficient technical knowledge and improper selection of strains, various problems such as clumping, odor, and mosquito and fly breeding are prone to occur.
Q :
Slow heating: the pile does not heat up or heats up slowly.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.The raw materials are too wet: add dry materials according to the material ratio and then stir and ferment.
2.The raw materials are too dry: According to the humidity, add water or wet materials to maintain the moisture at 45%-55%.
3.Insufficient nitrogen source: Add ammonium sulfate with high nitrogen content to maintain the carbon-nitrogen ratio at 20:1.
4.The pile is too small, or the weather is too cold: Pile the pile high and add easily degradable substances, such as corn stalks.
5.Do not add lime or plant ash to the pile or fermentation materials. Lime or plant ash has a bactericidal effect.
Q :
The pile temperature is too high: the pile temperature is ≥65 during the fermentation process.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.Poor air permeability: Turn the pile regularly to increase the air permeability of the fermentation pile.
2.The pile is too large: reduce the size of the pile.
Q :
Odor: There is a constant smell of rotten eggs or rotten smell coming from the pile.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.The ammonia content is too high (C/N less than 20): Use microbial deodorizer for disinfection and deodorization, and add high-carbon substances, such as crop straw, peanut shells, rice husks, etc.
2.Uneven ventilation or poor air flow: remix the materials and change the formula.
3.The materials are stacked too densely: remix the pile and add large particles as appropriate according to the density of the materials.
4.Anaerobic environment: Turn the pile regularly to increase the oxygen content in the pile.
Q :
Mosquitoes and flies breed: Mosquitoes and flies breed in the fermentation pile.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.The raw materials are stacked for too long before fermentation: Process the raw materials quickly and spray microbial deodorant on the surface to reduce odor and mosquitoes.
2. Fresh feces cover the surface of the pile and breeds mosquitoes and flies: turn the pile every 2-3 days.
Q :
Material agglomeration: The material in the pile has large parts and inconsistent structure.
A :
Possible causes and solutions:
1.Uneven mixing of raw materials or insufficient turning of piles: Improve the initial mixing method.
2.Uneven air flow or insufficient surroundings: sort or crush compost to improve air distribution.
3.The raw materials contain large pieces and non-degradable or slow-degrading materials: sort the compost, crush and organize the raw materials.
4.The composting process is not over: extend the fermentation time or improve the fermentation conditions.
Conclusion
In short, don’t worry if there are problems during the fermentation of organic fertilizer. First, find out the cause of the problem, and then find a suitable solution based on the cause of the problem and solve it as soon as possible. If the cause of the problem cannot be analyzed, do not deal with it blindly. You can consult an organic fertilizer fermentation expert and handle it according to the expert's guidance.