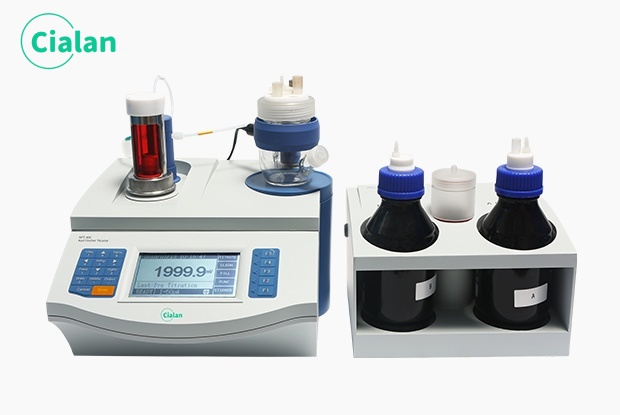
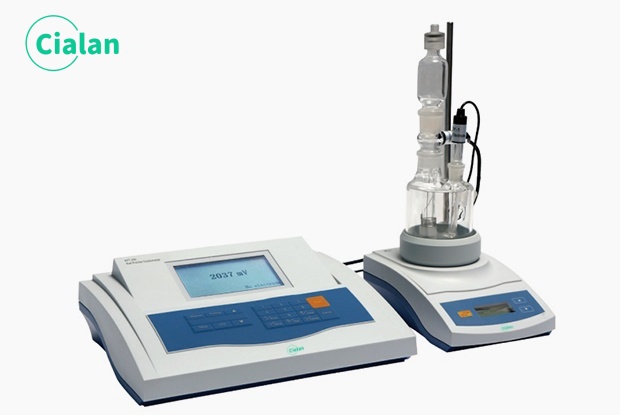
Why Every Lab Researcher Needs The Titration Equipment FAQ Guide
Are you an laboratory research operator, water industry investor, or pharmaceutical R&D staff selecting high- performance titration equipment? Whether you want to purchase a titrator for your lab or explore new equipment ideas for your research institutions,This FAQ Guide has everything you need.
This blog thoroughly addresses the most frequently asked questions about titrate equipment. From titration definition to calculating molarity, you’ll find reliable answers tailored to professionals like you. As automatic titrator equipment gains important for its widely usability, operating in options that meet global analysis standards and provide an easy experience for your researchers is essential.
We also examine how selecting the right titration gizmo can maximize your analytical requirement while minimizing maintenance costs. If you’re new to this field, the guide will help you navigate essential considerations such as types of titration, clean a burette, and select indicator.
Key topics covered include:
What Is Titration?
What Is Titration Used For?
What Is The Principle Of Titrator?
How To Choose A Right Titrator?
Don’t miss this opportunity to gain actionable insights that can turn your titration result into a higher precision. Read the Titration Equipment FAQ Guide now and elevate your analysis!

What Is Titration?
Titration is a quantitative method of chemical analysis in which the concentration of an analyte is calculated based on the chemical reaction between the analyte and the titrant by adding a known concentration of titrant to a solution of unknown concentration.
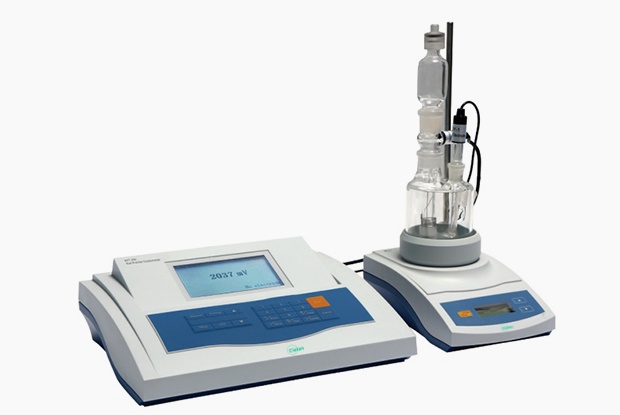

What Is Titration Used For?
Titrimetry is used for measuring the concentration of an unknown solution.

What Is The Analyte In A Titration?
In a titration reaction, the analyte, i.e., the titrand, is the substance in the solution to be measured in the amount or concentration to be determined.
The amount of analyte is usually calculated by a chemical reaction with the titrant during the chemical titration.

What Is The Principle Of Titrator?
The basic principle of titration chem is that a standard solution is added to the sample to be analyzed until the chemical reaction between the two reaches an end point and the concentration of the substance to be measured is calculated.

How To Calculate Molarity From Titration?
The generalized formula for titration calculations is:
C1=C2*V2*stoichiometric ratio/V1
Description of symbols:
C2/V2 : Concentration (mol/L) and volume (L) of the solution to be tested.
C1/V1 : Concentration (mol/L) and volume (L) of the standard solution.
Stoichiometric ratio: the ratio of the amount of substance of the substance to be measured to that of the standard, according to the chemical reaction equation.

How To Do Titration?
Titration Procedure
Use a pipette to accurately measure a certain volume of the solution to be measured and add it to the conical flask.
Add 2 to 3 drops of indicator such as phenolphthalein and observe the color change.
Add titrating solution to the buret.
Slowly add the titrant to the conical flask and shake until well mixed.
When the color of the indicator changes, slow down the addition of titrant until the end point is reached when the color of the indicator remains unchanged and stop the titrations.
Record the endpoint volume or titer.
Repeat the titration 3 times to maintain consistency of titer and to minimize errors.
Why Is Titration Important?
Titration has become an indispensable technique for quantitative chemical analysis by virtue of its high precision quantitative determination, wide range of chemical analysis fields, and diversity of titration methods. Whether for laboratory research, water quality testing or pharmaceutical production, titration provides the basic support for the analysis of substance concentration.
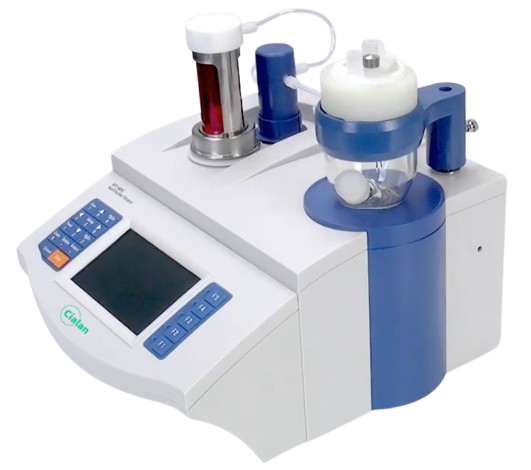

What Is A Titration Curve?
In practice, the titration curve is often used to reflect the process of titration analysis, which visualizes the changes in the concentration of the component to be measured in the solution with the addition of titrant. For example, acid-base titration of hydrogen ion concentration changes in solution, complexation titration changes in the concentration of metal ions to be measured, etc.
In addition, you can also use the instrument to measure the concentration of components related to a certain physical quantities, such as potential, current or absorbance, etc., so as to carry out a quantitative analysis, which belongs to the scope of the instrumental analysis method. Therefore, the titration curve is a function curve between the nature of the solution and the amount of titrant chemistry added during the titration process.
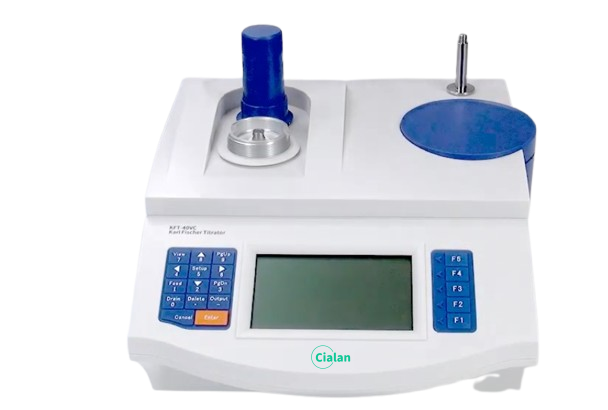

How To Read A Titration Curve?
Identification of critical areas such as the initial segment, the breakout zone and after the end point.
Determine the titration endpoint by instrumentation.
Acid-base, redox, and complexation titration curves are characterized differently.
Calculate concentrations, assess reaction feasibility and identify interferences.

Where Is The Buffer Region Of A Titration Curve?
In a titration curves, the buffer region is the interval in which the pH of the solution changes slowly, usually occurring during the titration of a weak acid or weak base.
The buffer region for the titration on weak acid strong base is located in the middle of the titration curve, where the pH is close to the pKa value of the weak acid, corresponding to the presence of a large number of weak acids and conjugate bases in the solution.
The buffer zone for the titration on weak base/strong acid is located in the middle of the titration curve, where the pH is close to the pKb corresponding to the pH of the weak base, corresponding to the presence of a large number of weak bases and conjugated acids in the solution.
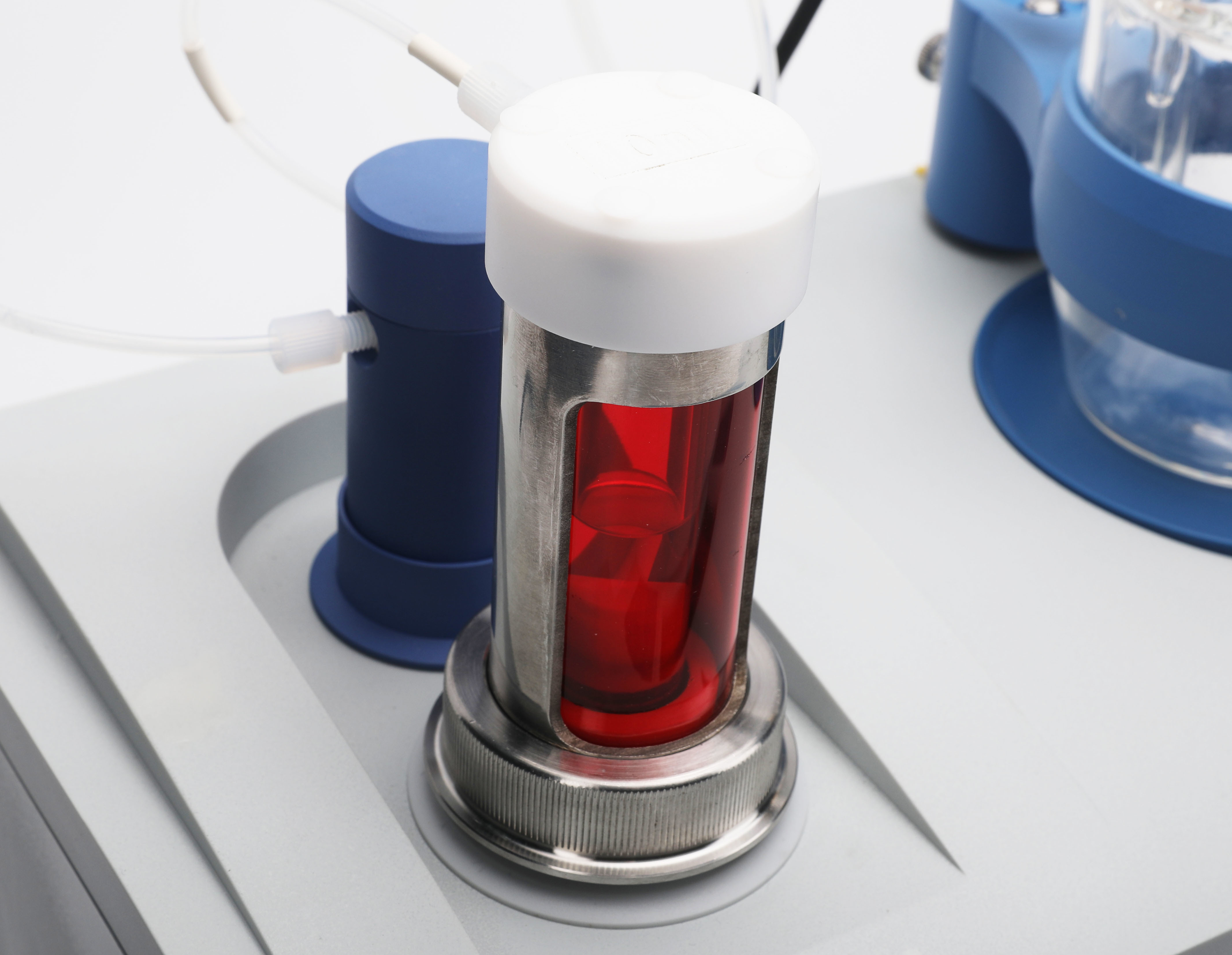

What Is Pka?
In a titration, pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant, which is intended to be a measure of the strength of the acid-how tightly the proton is bound by the Brownsted acid.
pKa = -lgKa
Ka : The dissociation constant of an acid, which indicates the ability of an acid to release protons in aqueous solution.
The smaller the pKa, the stronger the acid; the larger the pKa, the weaker the acid.
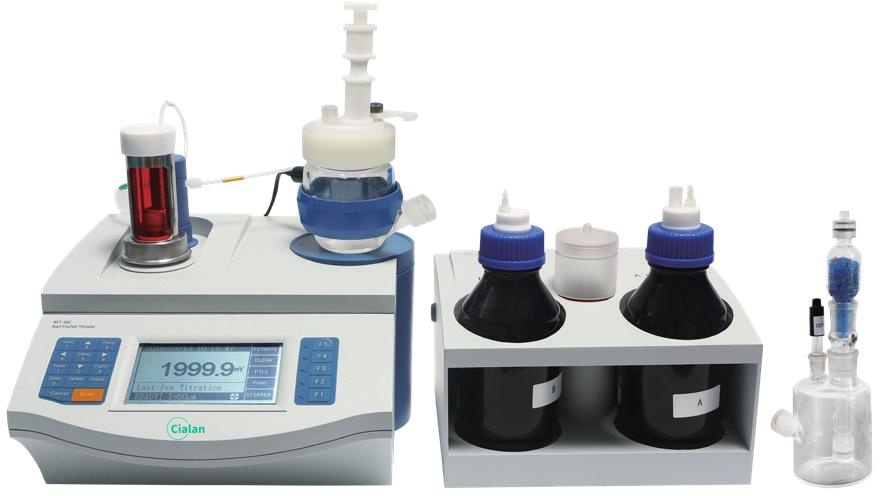
What Is The Relationship Between pKa And pH?
How To Find Pka From Titration Curve?
For the titration of weak acids or bases, pKa corresponds to the midpoint of the buffer region in the titration curve.
The interval in the titration curve where the pH changes gently is usually located between the start of the titration and the equivalence point.
The pH value corresponding to the midpoint of the buffer region is pKa.

What Is The Equivalence Point In A Titration?
In titration analysis, Equivalence Point is the theoretical point in a chemical reaction where the titrant and the analyte react completely according to stoichiometric ratios, at which time the amounts of moles of the two substances are exactly equal, which can be determined by indicators, instrumental tests, and titration curves.

What Is The Endpoint Of A Titration?
The endpoint is the point at which the indicator indicates completion of the titration by a change in color or intensity in the analyte solution.

Titration Endpoint VS Equivalence Point?

What Are The Four Types Of Titration?
Indirect titration is also known as Back Titration. Types of titrations in quantitative chemical analysis can be categorized into the following four main ways:
Acid-Base Titration
Redox Titration.
Complexation titrations.
Precipitation titrations.

Which Titration Is Better?
In analytical chemistry, acid base titration (neutralization titration) is the most commonly used form of titration.
Widely available acids and bases, such as foods and pharmaceuticals, can be directly determined by acid and base titration.
The reaction is fast and the end point is easy to determine.
Indicators are diverse and low-cost, such as phenolphthalein and methyl orange.
Only need to adjust the solution pH can be.

What Are The Titrimetry Analysis Methods?
Direct titration
Any component to be measured that can be titrated directly with a standard solution can be used for titrimetric analysis. Direct titration is simple, fast and accurate, and is the most commonly used and basic titration method in titrimetric analysis.
Back titration
When the chemical reaction is slow or the reactant is a solid added to the standard solution, the titration reaction is difficult to react immediately when the reaction is complete, can be used to return to the titration method.
Replacement titration
Some of the measured components can not be titrated directly, it can be reacted with another substance, replacement of a certain amount and then calculated by the measured components. Can be titrated to the substance, and then titrated with the appropriate titrant to be replaced by the amount of the substance.
Indirect titration
Some of the components to be measured can not be directly with the titrant chemical reaction, but can be with another can be produced with other titrant chemical reaction, then you can use indirect titration method.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Titration Machine?

What Indicator Is Best For Titration?
How To Choose An Indicator For A Titration?
Choose the indicator whose color change point and measurement point are as close to the same as possible
The sudden color change of the indicator at the endpoint is rapid and obvious.
It is convenient for the observer to make correct and timely judgment to reduce the endpoint error.

What Is The Function Of An Indicator In A Titration?
Indicator is a special class of reagents, mostly organic compounds, they are involved in the titration process in the titration reaction, generally due to the structure or composition of the change in the titrated solution caused by a rapid and obvious color change, if this sudden change occurs in the vicinity of the metering point, can play a role in indicating the end point.

Titrant VS Analyte VS Titrand VS Titrator VS Titrate VS Titer

Automatic Potentiometric Titrator VS. Karl Fischer Titrator
What Is A Primary Standard In Titration?
In titrimetric analysis, Primary Standard refers to a class of highly pure and stable chemical substances used to directly prepare standard solutions (titrants) or to calibrate the concentration of other solutions. It is the core foundation of accuracy in titration analysis and directly affects the reliability of experimental results.
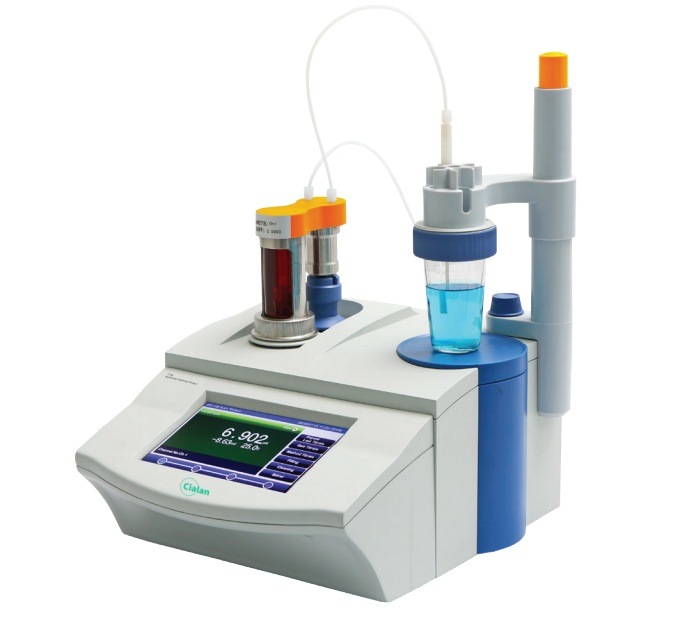

Why Does The Indicator Change Color In Titration?
Temperature:
Temperature changes, the color change range of the indicator also changes.
Solvent:
indicator in different solvents in the color change range is different.
The amount of indicator:
Concentration is small: the color change is sensitive;
Concentration is large: the end point of the color change is not sharp; The amount of indicator is better to use less.
Where To Dispose Titrant Solution?
Acid and alkali waste liquids need to be neutralized and then discharged.
Heavy metal-containing waste liquid should be collected separately and handed over to professional organizations for treatment.
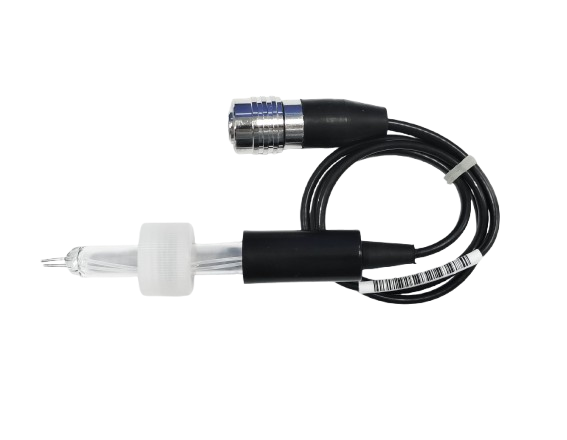
Why Are Titration Burette So Accurate?
The titration buret can accurately measure the volume of liquid, control the flow rate of the titrant, facilitate the indication of the end point judgment, reuse, and low maintenance costs.

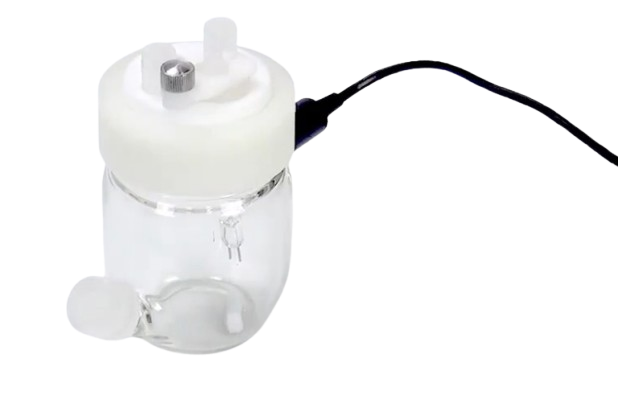
How To Clean A Burette?
Wash with distilled water, rinse with liquid to be filled.
Basic operation: close the piston of the buret, add 10ml of distilled water, tilt the mouth of the tube while rotating, so that the water is covered with water all over the inner wall of the tube, and then put the buret up, open the piston, release a part of the water, rinse the lower end of the buret, and then close the piston, the rest of the distilled water from the upper mouth pouring out, and repeat 2~3 times.
Note:
To avoid distilled water flowing out, put a beaker under the buret mouth;

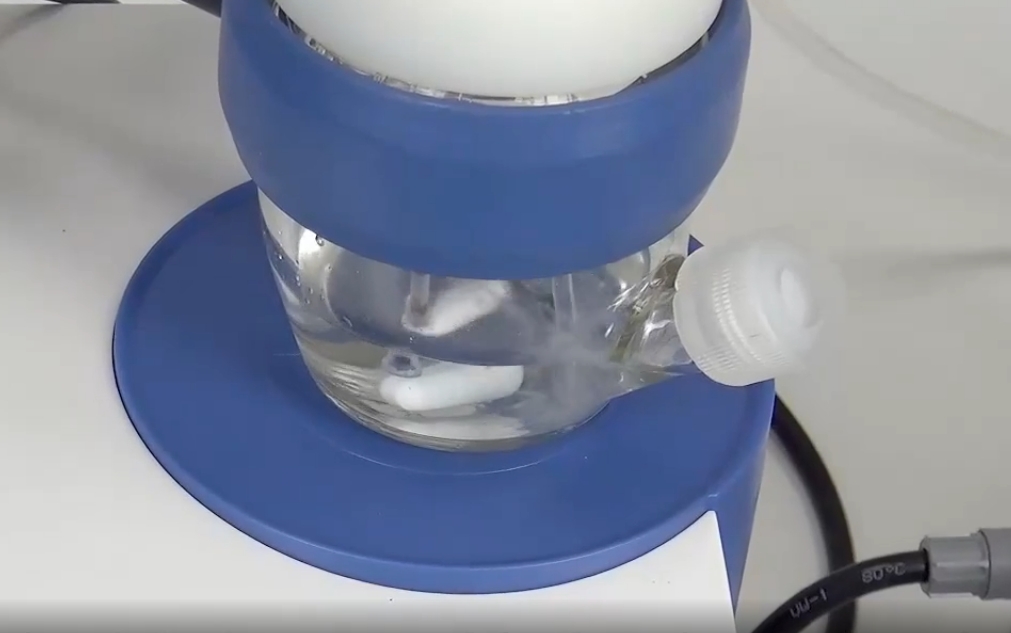
How Do You Remove Any Air Bubbles From The Burette?
Thoroughly clean the buret
Fill the buret vertically and control the speed
Ensure that the tip is free of contamination
Choose the right solution
Control the temperature and stabilize the operation

How To Improve Titration Accuracy?
Select high-precision titrator instruments and gauges such as burette, pipette, conical flask, volumetric flask, etc., correctly calibrate, rinse and fill
Accurately calibrate the reference material and store it away from light.
Control the titration speed and judge the end point accurately.
Titrate each sample at least 3 times to minimize errors.

How To Buy A Titrator Machine From China?
Importing titrator machine from China can be difficult for those who are new to international imports.
Purchasing from a reputable manufacturer and supplier eliminates hassle of logistics, as they handle the safe and reliable delivery of the product directly to your place.
When buying the titrators, it is important to keep the following points in mind:
1. Confirm that your selected supplier can securely export and deliver the machine, and ensure that your agreement includes all essential shipping information.
2. Choose the delivery way (by sea, air, or express) based on your preference.
3. Remember to factor in duty imports and taxes when calculating the total cost.

How Does a Manufacturer Deliver The Auto Titrator?
Safe shipping is so important as quality manufacturing.
A responsible manufacturer should deliver your conduct meter safely.
Most autotitrator manufacturers use export cartoon case to pack the device.
You should read all the necessary instructions available on the sides of the boxes before boxing.
Is There Any Warranty On Ttitrant Titrator?
For optimal performance, it is important to regularly maintain your equipment for titration, so it can operate efficiently for an extended period. It is essential to be aware of the warranty coverage for your equipment, as it ensures that any manufacturing issues will be repaired at no additional cost by the supplier. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase a titration machine from a manufacturer that offers warranty services —Cialan.
Reputable titrator manufacturers typically provide a 1-year warranty. for example, offers complimentary repair and maintenance services during the first year.
Before purchasing a titrator, it is advisable to review the warranty period and other associated terms and conditions.
What After-Sale Service Does A Titrator Units Provide?
The reliable china titrator suppliers offers the following after-sale services:
1. Secure product delivery.
2. Thorough inspection prior to installation.
3. Complimentary online guidance for device installation and maintenance.
4. Free training for your users.
5. Regular assessments of your titrator equipment.
Can You Do OEM&ODM For Titrator?
Yes, Cialan can do OEM#OEM for our users, just send us your requirements for titrator equipment.

Where To Find Titrator Manufacturers?
Numerous online directories can connect you with titrator manufacturers.
A simple search for "top-rated laboratory titrator manufacturers" yields multiple options. However, it's essential to exercise caution when selecting a manufacturer from online search results. Before making a decision, conduct thorough research on the company's background and reputation. Look up reviews on “Google” and reputable review sites to gauge their credibility.
Additionally, It's also crucial to review their portfolio of request that potential manufacturers share examples of their previous work to ensure they meet your standards.

How To Choose A Right Titrator?
What is the sample to be measured?
What parameters are to be measured?
What is the measurement range?
What is the measurement accuracy required?
What is the budget?

What Should You Look For In Good Titrator?
The best titrator needs to meet the core requirements of high accuracy, repeatability, simplicity of operation, variety of titration methods and data reliability.
This blog thoroughly addresses the most frequently asked questions about titrate equipment. From titration definition to calculating molarity, you’ll find reliable answers tailored to professionals like you. As automatic titrator equipment gains important for its widely usability, operating in options that meet global analysis standards and provide an easy experience for your researchers is essential.
We also examine how selecting the right titration gizmo can maximize your analytical requirement while minimizing maintenance costs. If you’re new to this field, the guide will help you navigate essential considerations such as types of titration, clean a burette, and select indicator.
Key topics covered include:
What Is Titration?
What Is Titration Used For?
What Is The Principle Of Titrator?
How To Choose A Right Titrator?
Don’t miss this opportunity to gain actionable insights that can turn your titration result into a higher precision. Read the Titration Equipment FAQ Guide now and elevate your analysis!

What Is Titration?
Titration is a quantitative method of chemical analysis in which the concentration of an analyte is calculated based on the chemical reaction between the analyte and the titrant by adding a known concentration of titrant to a solution of unknown concentration.

What Is Titration Used For?
Titrimetry is used for measuring the concentration of an unknown solution.

What Is The Analyte In A Titration?
In a titration reaction, the analyte, i.e., the titrand, is the substance in the solution to be measured in the amount or concentration to be determined.
The amount of analyte is usually calculated by a chemical reaction with the titrant during the chemical titration.

What Is The Principle Of Titrator?
The basic principle of titration chem is that a standard solution is added to the sample to be analyzed until the chemical reaction between the two reaches an end point and the concentration of the substance to be measured is calculated.

How To Calculate Molarity From Titration?
The generalized formula for titration calculations is:
C1=C2*V2*stoichiometric ratio/V1
Description of symbols:
C2/V2 : Concentration (mol/L) and volume (L) of the solution to be tested.
C1/V1 : Concentration (mol/L) and volume (L) of the standard solution.
Stoichiometric ratio: the ratio of the amount of substance of the substance to be measured to that of the standard, according to the chemical reaction equation.

How To Do Titration?
Titration Procedure
Use a pipette to accurately measure a certain volume of the solution to be measured and add it to the conical flask.
Add 2 to 3 drops of indicator such as phenolphthalein and observe the color change.
Add titrating solution to the buret.
Slowly add the titrant to the conical flask and shake until well mixed.
When the color of the indicator changes, slow down the addition of titrant until the end point is reached when the color of the indicator remains unchanged and stop the titrations.
Record the endpoint volume or titer.
Repeat the titration 3 times to maintain consistency of titer and to minimize errors.

Why Is Titration Important?
Titration has become an indispensable technique for quantitative chemical analysis by virtue of its high precision quantitative determination, wide range of chemical analysis fields, and diversity of titration methods. Whether for laboratory research, water quality testing or pharmaceutical production, titration provides the basic support for the analysis of substance concentration.

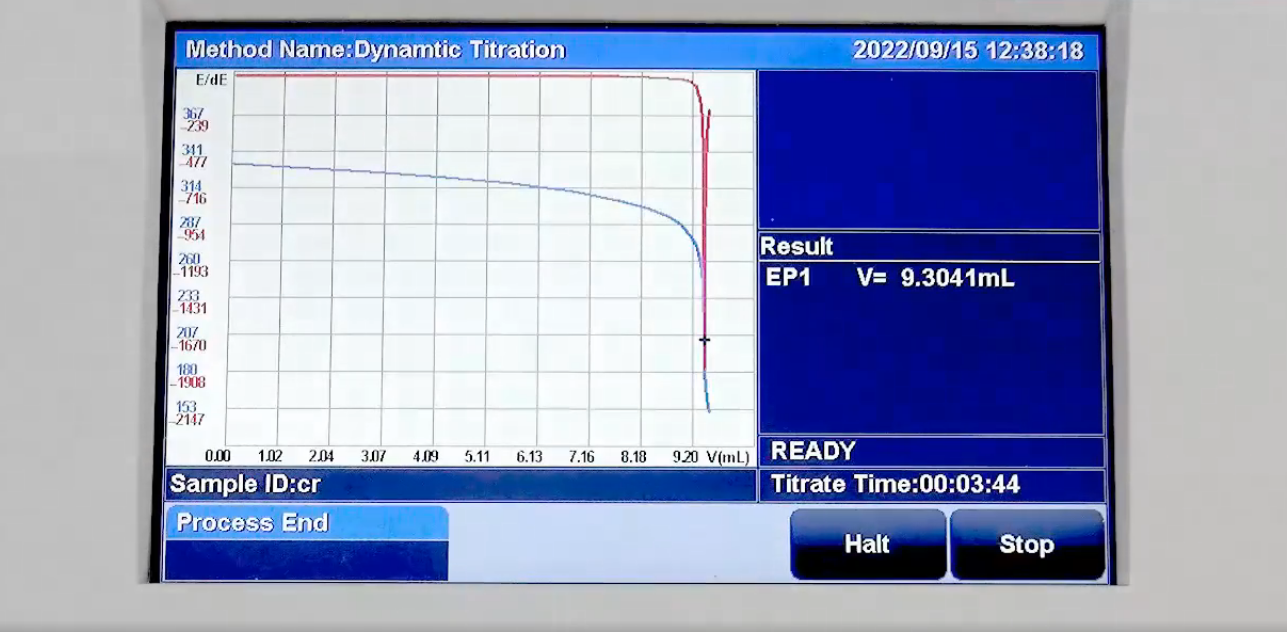
What Is A Titration Curve?
In practice, the titration curve is often used to reflect the process of titration analysis, which visualizes the changes in the concentration of the component to be measured in the solution with the addition of titrant. For example, acid-base titration of hydrogen ion concentration changes in solution, complexation titration changes in the concentration of metal ions to be measured, etc.
In addition, you can also use the instrument to measure the concentration of components related to a certain physical quantities, such as potential, current or absorbance, etc., so as to carry out a quantitative analysis, which belongs to the scope of the instrumental analysis method. Therefore, the titration curve is a function curve between the nature of the solution and the amount of titrant chemistry added during the titration process.

How To Read A Titration Curve?
Identification of critical areas such as the initial segment, the breakout zone and after the end point.
Determine the titration endpoint by instrumentation.
Acid-base, redox, and complexation titration curves are characterized differently.
Calculate concentrations, assess reaction feasibility and identify interferences.

Where Is The Buffer Region Of A Titration Curve?
In a titration curves, the buffer region is the interval in which the pH of the solution changes slowly, usually occurring during the titration of a weak acid or weak base.
The buffer region for the titration on weak acid strong base is located in the middle of the titration curve, where the pH is close to the pKa value of the weak acid, corresponding to the presence of a large number of weak acids and conjugate bases in the solution.
The buffer zone for the titration on weak base/strong acid is located in the middle of the titration curve, where the pH is close to the pKb corresponding to the pH of the weak base, corresponding to the presence of a large number of weak bases and conjugated acids in the solution.

What Is Pka?
In a titration, pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant, which is intended to be a measure of the strength of the acid-how tightly the proton is bound by the Brownsted acid.
pKa = -lgKa
Ka : The dissociation constant of an acid, which indicates the ability of an acid to release protons in aqueous solution.
The smaller the pKa, the stronger the acid; the larger the pKa, the weaker the acid.

What Is The Relationship Between pKa And pH?
| Relationship | Difference |
| Henderson-Hasselbalch equation pH = pka+lg ([A–]/[HA]) |
pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in an aqueous solution. Negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration. pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant, determines the behavior of a molecule at a specific pH. |

How To Find Pka From Titration Curve?
For the titration of weak acids or bases, pKa corresponds to the midpoint of the buffer region in the titration curve.
The interval in the titration curve where the pH changes gently is usually located between the start of the titration and the equivalence point.
The pH value corresponding to the midpoint of the buffer region is pKa.

What Is The Equivalence Point In A Titration?
In titration analysis, Equivalence Point is the theoretical point in a chemical reaction where the titrant and the analyte react completely according to stoichiometric ratios, at which time the amounts of moles of the two substances are exactly equal, which can be determined by indicators, instrumental tests, and titration curves.

What Is The Endpoint Of A Titration?
The endpoint is the point at which the indicator indicates completion of the titration by a change in color or intensity in the analyte solution.

Titration Endpoint VS Equivalence Point?
| Endpoint | Equivalence Point |
| The endpoint occurs after the equivocal point. The point at which the indicator changes color Can be observed directly |
The point of complete reaction of the indicator with the analyte. Cannot be observed directly and needs to be calculated. |

What Are The Four Types Of Titration?
Indirect titration is also known as Back Titration. Types of titrations in quantitative chemical analysis can be categorized into the following four main ways:
Acid-Base Titration
Redox Titration.
Complexation titrations.
Precipitation titrations.
| Acid-Base Titration | Determination of acid/base concentration based on the neutralization reaction between acid and base. Such as determination of acidity and alkalinity of industrial wastewater. |
| Redox Titration | A redox titration is also known as a oxidation-reduction titrations reaction. It occurs between the analyte and the titrant and electrons are transferred. Such as analysis of vitamin C content. |
| Complexation titrations | Complexation titration uses a ligand to form a stable complex with a metal ion, often EDTA. Such as water hardness test. |
| Precipitation titrations | Two substances react to produce an insoluble precipitate.Such as determination of chloride ions in drinking water or table salt |

Which Titration Is Better?
In analytical chemistry, acid base titration (neutralization titration) is the most commonly used form of titration.
Widely available acids and bases, such as foods and pharmaceuticals, can be directly determined by acid and base titration.
The reaction is fast and the end point is easy to determine.
Indicators are diverse and low-cost, such as phenolphthalein and methyl orange.
Only need to adjust the solution pH can be.

What Are The Titrimetry Analysis Methods?
Direct titration
Any component to be measured that can be titrated directly with a standard solution can be used for titrimetric analysis. Direct titration is simple, fast and accurate, and is the most commonly used and basic titration method in titrimetric analysis.
Back titration
When the chemical reaction is slow or the reactant is a solid added to the standard solution, the titration reaction is difficult to react immediately when the reaction is complete, can be used to return to the titration method.
Replacement titration
Some of the measured components can not be titrated directly, it can be reacted with another substance, replacement of a certain amount and then calculated by the measured components. Can be titrated to the substance, and then titrated with the appropriate titrant to be replaced by the amount of the substance.
Indirect titration
Some of the components to be measured can not be directly with the titrant chemical reaction, but can be with another can be produced with other titrant chemical reaction, then you can use indirect titration method.

What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Titration Machine?
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Automatic control of titration speed by electrode or potentiometer, more accurate endpoint judgment, reducing human error. Automatic liquid addition, stirring, data recording and analysis. Various types of titration: acid-base titration, redox titration, complex titration, precipitation titration. Automatic generation of titration curve, calculation of concentration, easy to save data. |
Higher instrument purchase and maintenance costs. Specialized training is required for proficient operation. Time-consuming instrument calibration and troubleshooting. Poor adaptability to turbid, colored or highly viscous samples. Electrodes and tubing require periodic cleaning and calibration. Increased cost of reagents and consumables. |

What Indicator Is Best For Titration?
| Acid Base Titrations Indicator | Phenolphthalein Color change range: pH 8.0 (colorless) → 10.0 (red) Usage: Commonly used for reactions with alkaline endpoints. Methyl Orange Color discoloration range: pH 3.1 (red) → 4.4 (orange) Usage: Often used when the endpoint is acidic. |
Redox Titration Indicator |
Starch Usage: Forms a dark blue complex with iodine (I₂) to indicate the end point of the reaction. Potassium permanganate: under acidic conditions, purple → colorless, without additional indicator. |
| Complexation titration indicator (EDTA titration) | Chromium Black T (Eriochrome Black T, EBT) pH: 8-11 Color change: red→blue, used for titration of metal ions such as Ca²⁺ and Mg²⁺. |
| Precipitation Titration Indicator | Fluorescent Yellow (Adsorption Indicator) Purpose: The precipitation adsorption indicator turns pink at the end of the reaction. |

How To Choose An Indicator For A Titration?
Choose the indicator whose color change point and measurement point are as close to the same as possible
The sudden color change of the indicator at the endpoint is rapid and obvious.
It is convenient for the observer to make correct and timely judgment to reduce the endpoint error.

What Is The Function Of An Indicator In A Titration?
Indicator is a special class of reagents, mostly organic compounds, they are involved in the titration process in the titration reaction, generally due to the structure or composition of the change in the titrated solution caused by a rapid and obvious color change, if this sudden change occurs in the vicinity of the metering point, can play a role in indicating the end point.

Titrant VS Analyte VS Titrand VS Titrator VS Titrate VS Titer
| Titrant | A standard solution of known concentration that is added drop by drop to an analyte solution through a buret. |
| Analyte | A sample to be tested whose concentration or content needs to be determined by titration. |
| Titrand | Titrand is the component of the solution to be measured that is to be quantitatively analyzed, i.e. the target analyte. It is determined by reacting with Titrant. |
| Titrator | A titrator is an instrument that automatically detects the endpoint of a reaction by precisely controlling the amount of titrant added. |
| Titrate | Verb: refers to the process of performing a titration (e.g., “titrate a solution”). |
| Titer | Titer is a way of expressing the concentration of a standard solution in a titration analysis, and is often used to quickly calculate the concentration of a substance being measured. |

Automatic Potentiometric Titrator VS. Karl Fischer Titrator
| Potentiometric Titrator | Karl Fischer Titrator |
| Widely used for acid-base titrations, redox titrations, complexation titrations. The end point is determined by monitoring the change in potential of the solution during the titration. |
Determination of moisture Based on Karl Fischer reaction, the end point is determined by the galvanometric method. |

What Is A Primary Standard In Titration?
In titrimetric analysis, Primary Standard refers to a class of highly pure and stable chemical substances used to directly prepare standard solutions (titrants) or to calibrate the concentration of other solutions. It is the core foundation of accuracy in titration analysis and directly affects the reliability of experimental results.

Why Does The Indicator Change Color In Titration?
Temperature:
Temperature changes, the color change range of the indicator also changes.
Solvent:
indicator in different solvents in the color change range is different.
The amount of indicator:
Concentration is small: the color change is sensitive;
Concentration is large: the end point of the color change is not sharp; The amount of indicator is better to use less.

Where To Dispose Titrant Solution?
Acid and alkali waste liquids need to be neutralized and then discharged.
Heavy metal-containing waste liquid should be collected separately and handed over to professional organizations for treatment.

Why Are Titration Burette So Accurate?
The titration buret can accurately measure the volume of liquid, control the flow rate of the titrant, facilitate the indication of the end point judgment, reuse, and low maintenance costs.

How To Clean A Burette?
Wash with distilled water, rinse with liquid to be filled.
Basic operation: close the piston of the buret, add 10ml of distilled water, tilt the mouth of the tube while rotating, so that the water is covered with water all over the inner wall of the tube, and then put the buret up, open the piston, release a part of the water, rinse the lower end of the buret, and then close the piston, the rest of the distilled water from the upper mouth pouring out, and repeat 2~3 times.
Note:
To avoid distilled water flowing out, put a beaker under the buret mouth;

How Do You Remove Any Air Bubbles From The Burette?
Thoroughly clean the buret
Fill the buret vertically and control the speed
Ensure that the tip is free of contamination
Choose the right solution
Control the temperature and stabilize the operation

How To Improve Titration Accuracy?
Select high-precision titrator instruments and gauges such as burette, pipette, conical flask, volumetric flask, etc., correctly calibrate, rinse and fill
Accurately calibrate the reference material and store it away from light.
Control the titration speed and judge the end point accurately.
Titrate each sample at least 3 times to minimize errors.

How To Buy A Titrator Machine From China?
Importing titrator machine from China can be difficult for those who are new to international imports.
Purchasing from a reputable manufacturer and supplier eliminates hassle of logistics, as they handle the safe and reliable delivery of the product directly to your place.
When buying the titrators, it is important to keep the following points in mind:
1. Confirm that your selected supplier can securely export and deliver the machine, and ensure that your agreement includes all essential shipping information.
2. Choose the delivery way (by sea, air, or express) based on your preference.
3. Remember to factor in duty imports and taxes when calculating the total cost.

How Does a Manufacturer Deliver The Auto Titrator?
Safe shipping is so important as quality manufacturing.
A responsible manufacturer should deliver your conduct meter safely.
Most autotitrator manufacturers use export cartoon case to pack the device.
You should read all the necessary instructions available on the sides of the boxes before boxing.

Is There Any Warranty On Ttitrant Titrator?
For optimal performance, it is important to regularly maintain your equipment for titration, so it can operate efficiently for an extended period. It is essential to be aware of the warranty coverage for your equipment, as it ensures that any manufacturing issues will be repaired at no additional cost by the supplier. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase a titration machine from a manufacturer that offers warranty services —Cialan.
Reputable titrator manufacturers typically provide a 1-year warranty. for example, offers complimentary repair and maintenance services during the first year.
Before purchasing a titrator, it is advisable to review the warranty period and other associated terms and conditions.

What After-Sale Service Does A Titrator Units Provide?
The reliable china titrator suppliers offers the following after-sale services:
1. Secure product delivery.
2. Thorough inspection prior to installation.
3. Complimentary online guidance for device installation and maintenance.
4. Free training for your users.
5. Regular assessments of your titrator equipment.

Can You Do OEM&ODM For Titrator?
Yes, Cialan can do OEM#OEM for our users, just send us your requirements for titrator equipment.

Where To Find Titrator Manufacturers?
Numerous online directories can connect you with titrator manufacturers.
A simple search for "top-rated laboratory titrator manufacturers" yields multiple options. However, it's essential to exercise caution when selecting a manufacturer from online search results. Before making a decision, conduct thorough research on the company's background and reputation. Look up reviews on “Google” and reputable review sites to gauge their credibility.
Additionally, It's also crucial to review their portfolio of request that potential manufacturers share examples of their previous work to ensure they meet your standards.

How To Choose A Right Titrator?
What is the sample to be measured?
What parameters are to be measured?
What is the measurement range?
What is the measurement accuracy required?
What is the budget?

What Should You Look For In Good Titrator?
The best titrator needs to meet the core requirements of high accuracy, repeatability, simplicity of operation, variety of titration methods and data reliability.