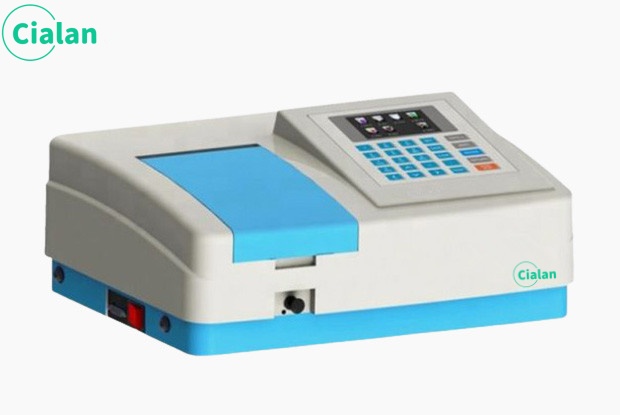
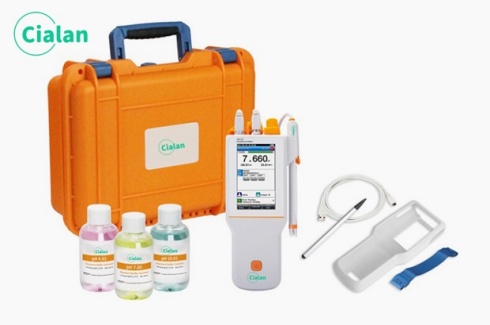
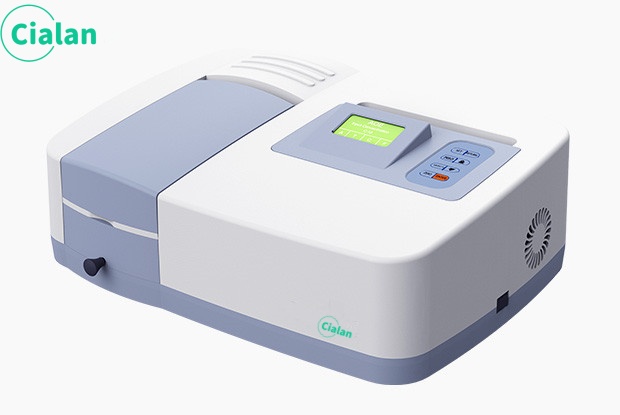
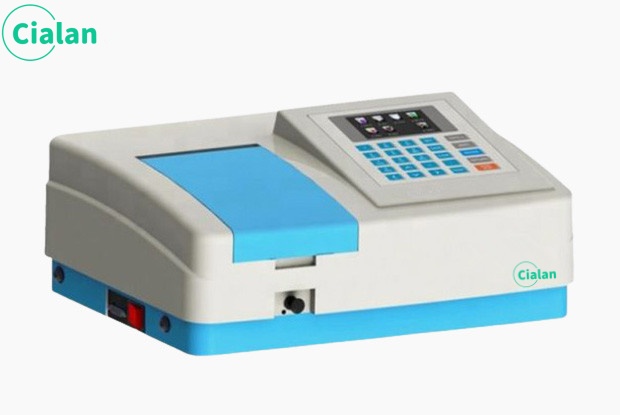
Wavelength range area of a spectrophotometer.
Wavelength range area of a spectrophotometer.
It includes the visible light region with a wavelength range of 400~760nm and the ultraviolet light region with a wavelength range of 200~400nm. Different light sources have emission spectra, so different illuminants can be used as the light source of the instrument.

How it works?
The spectrophotometer uses a light source that can be multiple wavelengths. It uses a series of spectroscopic devices to produce a light source of a specific wavelength. After the light source passes through the tested sample, part of the light source is absorbed, and the absorbance value of the sample is calculated, thereby converting it into concentration. The absorbance value of the sample is directly proportional to the concentration of the sample.
What does it measure?
A spectrophotometer or a spectrometer, is a scientific instrument that decomposes light with complex components into spectral lines. Spectrophotometry is the qualitative or quantitative analysis of the substance based on the absorbance of light at a specific wavelength or within a certain wavelength range. Commonly used wavelength ranges are: ultraviolet light region of 200 ~ 380nm, visible light region of 380 ~ 780nm, infrared light region of 2.5 ~ 25um (4000cm ~ 400cm based on wave number).
The instruments used are ultraviolet spectrophotometer and visible light spectrophotometer. IR spectrophotometer or AAS atomic absorption spectrophotometer. In order to ensure the precision and accuracy of measurement, all instruments should be regularly calibrated and calibrated in accordance with national metrological calibration regulations or this appendix.
Configuration.
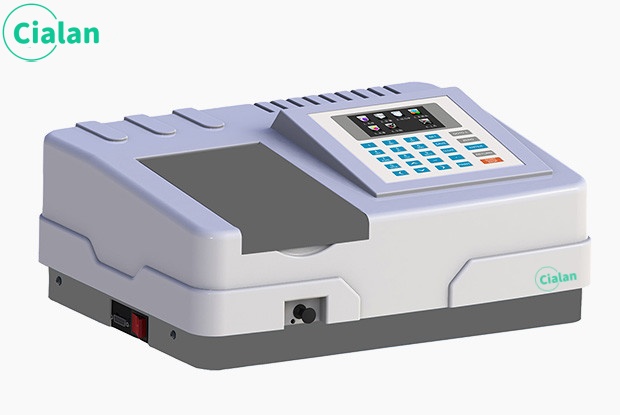
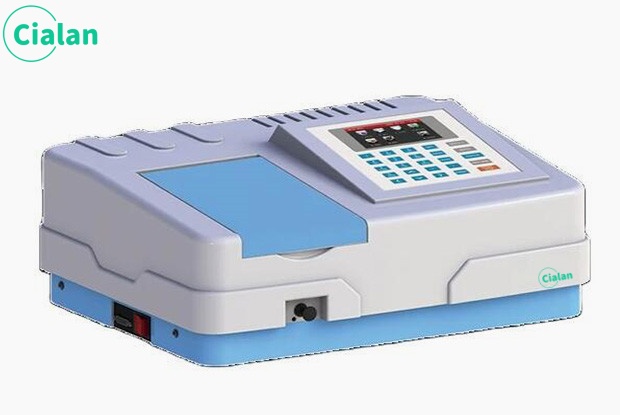
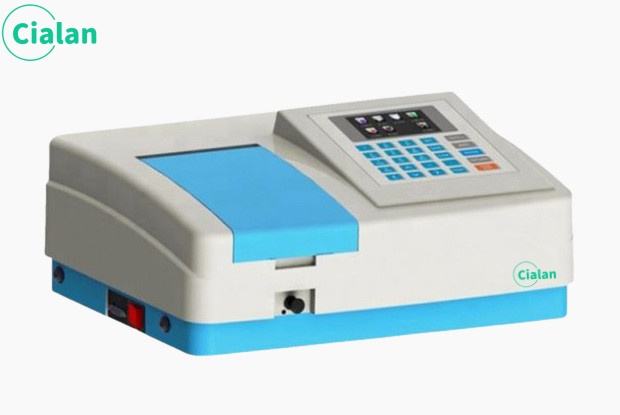
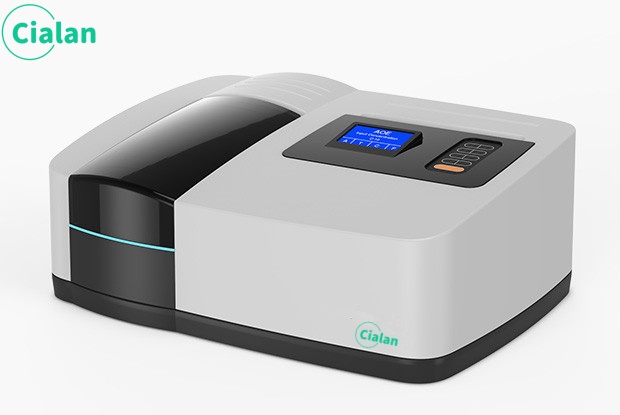
The instrument mainly consists of a light source monochromator, sample chamber, detector, signal processor and display and storage system.
It includes the visible light region with a wavelength range of 400~760nm and the ultraviolet light region with a wavelength range of 200~400nm. Different light sources have emission spectra, so different illuminants can be used as the light source of the instrument.

How it works?
The spectrophotometer uses a light source that can be multiple wavelengths. It uses a series of spectroscopic devices to produce a light source of a specific wavelength. After the light source passes through the tested sample, part of the light source is absorbed, and the absorbance value of the sample is calculated, thereby converting it into concentration. The absorbance value of the sample is directly proportional to the concentration of the sample.
What does it measure?
A spectrophotometer or a spectrometer, is a scientific instrument that decomposes light with complex components into spectral lines. Spectrophotometry is the qualitative or quantitative analysis of the substance based on the absorbance of light at a specific wavelength or within a certain wavelength range. Commonly used wavelength ranges are: ultraviolet light region of 200 ~ 380nm, visible light region of 380 ~ 780nm, infrared light region of 2.5 ~ 25um (4000cm ~ 400cm based on wave number).
The instruments used are ultraviolet spectrophotometer and visible light spectrophotometer. IR spectrophotometer or AAS atomic absorption spectrophotometer. In order to ensure the precision and accuracy of measurement, all instruments should be regularly calibrated and calibrated in accordance with national metrological calibration regulations or this appendix.
Configuration.
The instrument mainly consists of a light source monochromator, sample chamber, detector, signal processor and display and storage system.