What is the Kjeldahl method for nitrogen determination?
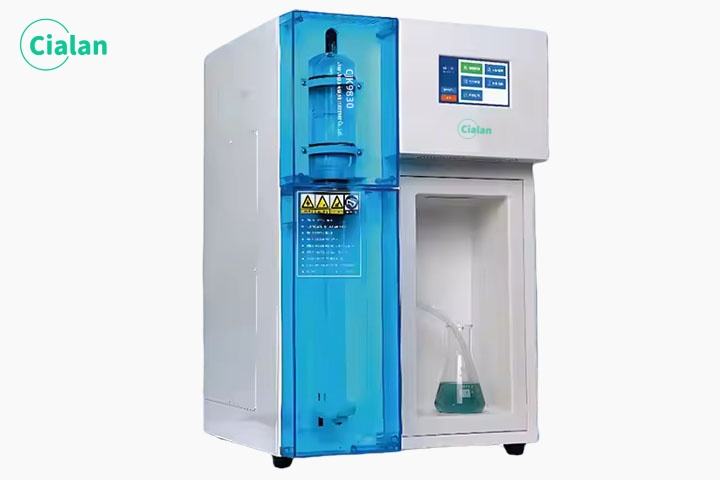
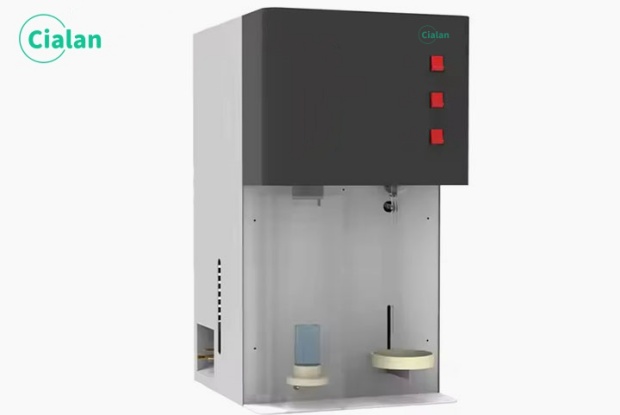
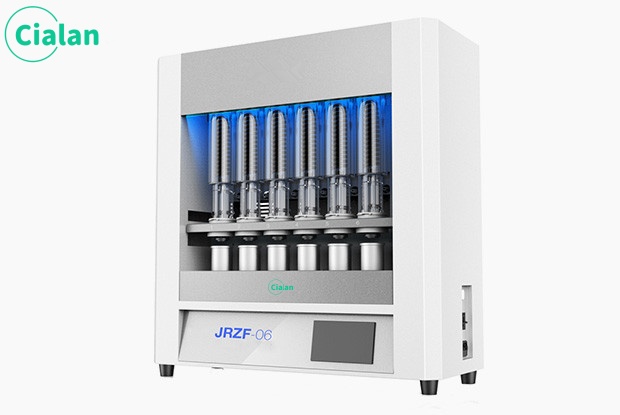
Kjeldahl nitrogen analyzer is a common analytical instrument used to measure the total nitrogen content in samples. It is widely used in environmental monitoring, agricultural science, biomedicine and other fields. As an important component, its core technologies include photometry, evaporation concentration, infrared absorption technology, etc. This article will introduce the basic principles, workflow, and advantages of the instrument from the perspective of the manufacturer.

Basic principles.
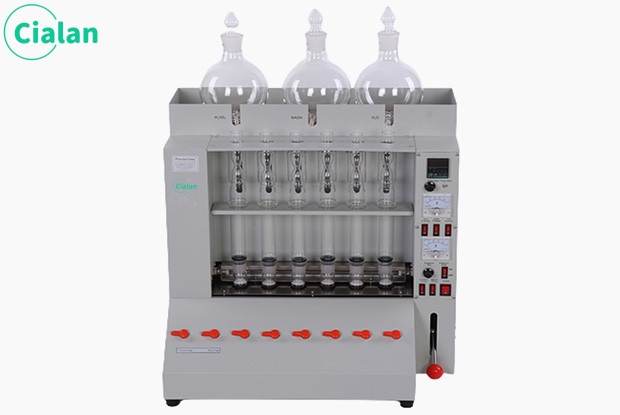
It converts the organic nitrogen in the sample into ammonia under high temperature and alkaline conditions, and then collects the ammonia with sulfuric acid under acidic conditions. Finally, its concentration is measured by titration or colorimetry to calculate the total nitrogen content in the sample. This method is applicable to almost all types of samples, including plants, soil, water, fertilizers, food, etc.
Working process.
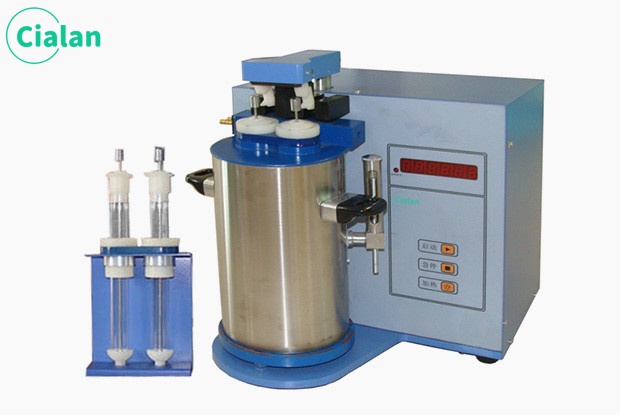
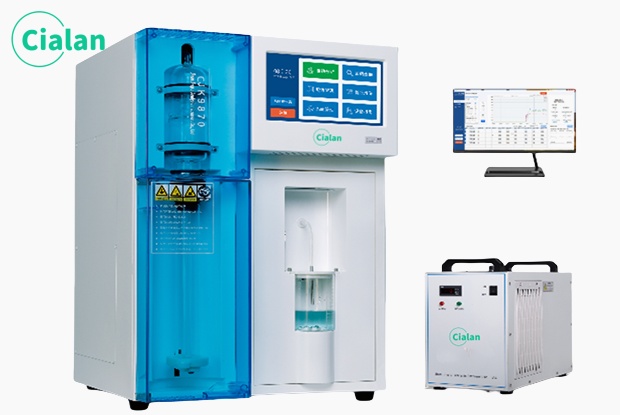
The workflow is divided into steps such as sample preparation, heating digestion, evaporation concentration, ammonia collection and measurement. Among them, sample preparation is a key link. The sample needs to be added to the test tube and an appropriate amount of reagents, such as sulfuric acid, nitration catalyst, etc., and then shaken or sonicated to promote the reaction. Next, the sample is digested under high temperature and alkaline conditions to convert organic nitrogen into ammonia. Then, the ammonia is collected into the sulfuric acid solution by evaporation and concentration, and the ammonia content is determined by titration or colorimetry. Finally, the total nitrogen content in the sample was calculated based on the ammonia content.
Advantages.
1. The total nitrogen content in the sample can be measured quickly and accurately;
2. It has a wide range of applications and can analyze almost all types of samples;
3. The operation is simple and requires less special skills and experience;
4. The cost is relatively low.

Basic principles.
It converts the organic nitrogen in the sample into ammonia under high temperature and alkaline conditions, and then collects the ammonia with sulfuric acid under acidic conditions. Finally, its concentration is measured by titration or colorimetry to calculate the total nitrogen content in the sample. This method is applicable to almost all types of samples, including plants, soil, water, fertilizers, food, etc.
Working process.
The workflow is divided into steps such as sample preparation, heating digestion, evaporation concentration, ammonia collection and measurement. Among them, sample preparation is a key link. The sample needs to be added to the test tube and an appropriate amount of reagents, such as sulfuric acid, nitration catalyst, etc., and then shaken or sonicated to promote the reaction. Next, the sample is digested under high temperature and alkaline conditions to convert organic nitrogen into ammonia. Then, the ammonia is collected into the sulfuric acid solution by evaporation and concentration, and the ammonia content is determined by titration or colorimetry. Finally, the total nitrogen content in the sample was calculated based on the ammonia content.
Advantages.
1. The total nitrogen content in the sample can be measured quickly and accurately;
2. It has a wide range of applications and can analyze almost all types of samples;
3. The operation is simple and requires less special skills and experience;
4. The cost is relatively low.